In this guide, you will learn:
- Two different ways to store data with Tulip
- When to use different data storage methods
- The importance of adopting a data model
When working with data, maintaining organization is crucial to avoid clutter and centralize information. With Tulip, storing and managing your data is made easy with multiple options based on your needs.
How does Tulip data capture your operations?
Data exists at multiple levels in Tulip.
Apps store static data, like text instructions on a step.
Tables are Tulip-built databases, like a spreadsheet of work orders, you can use across multiple apps.
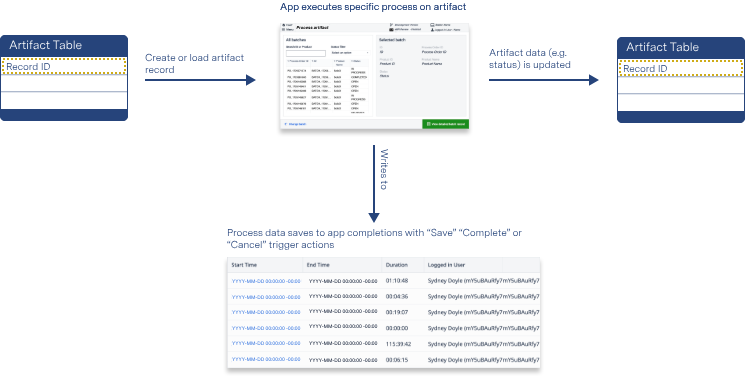
Completions store production metadata, such as app duration, station name, and any input data to variables.
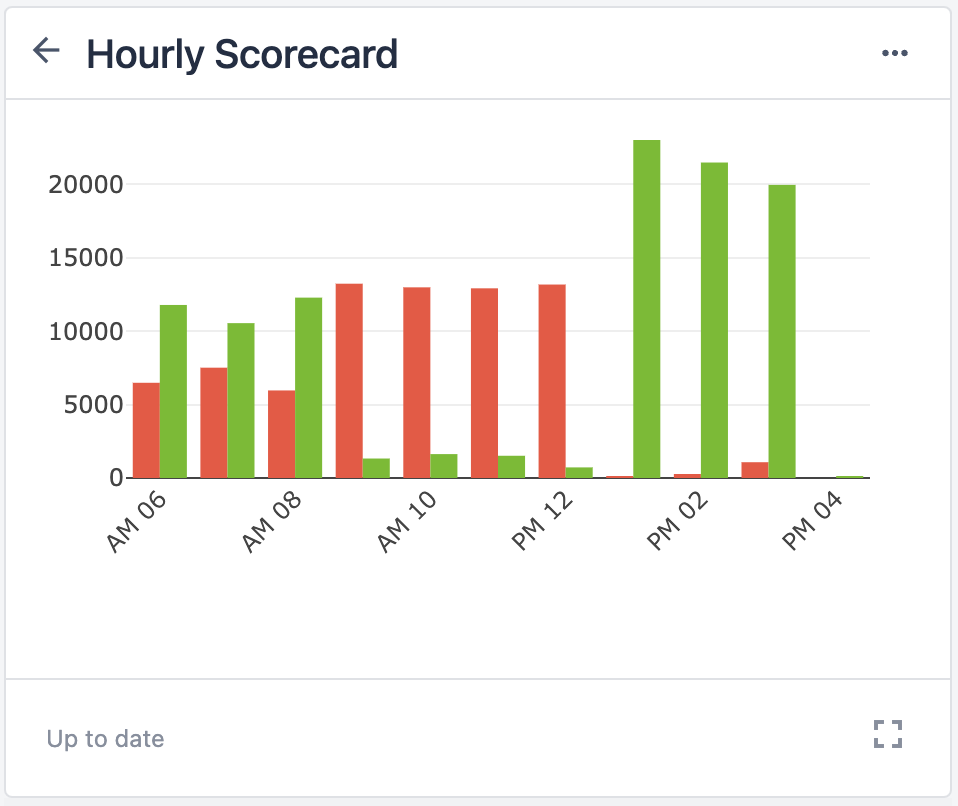
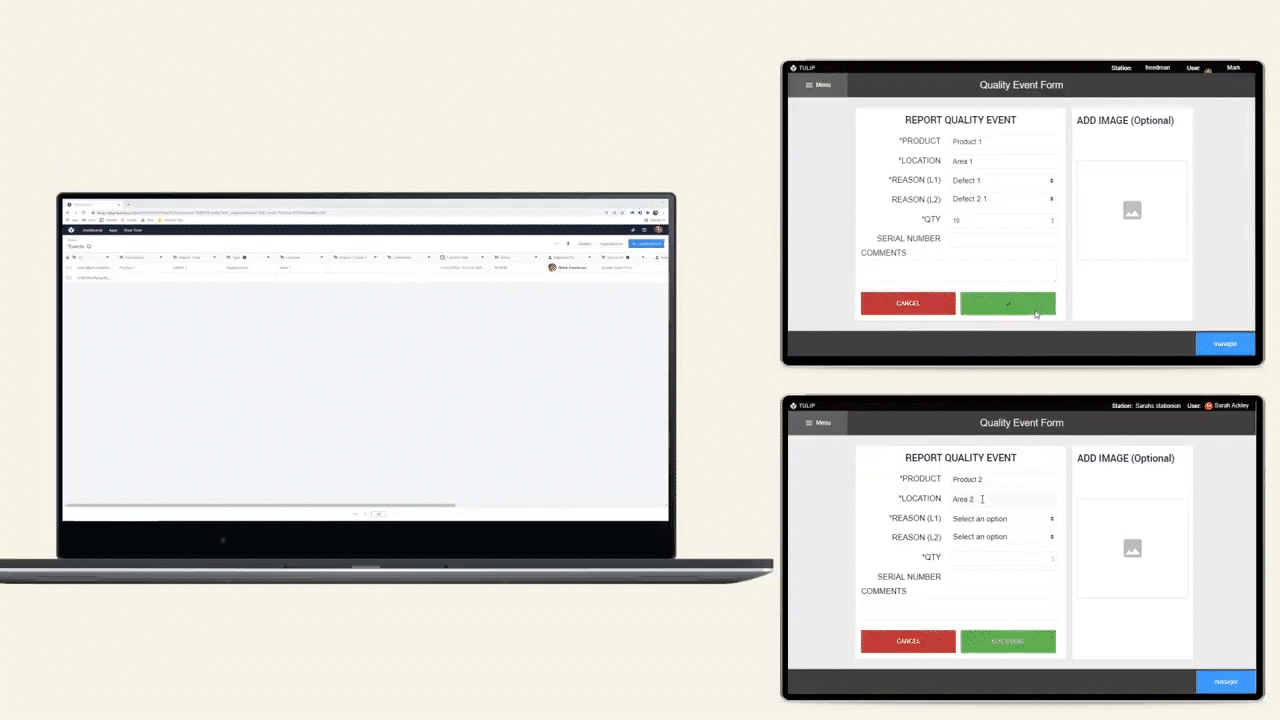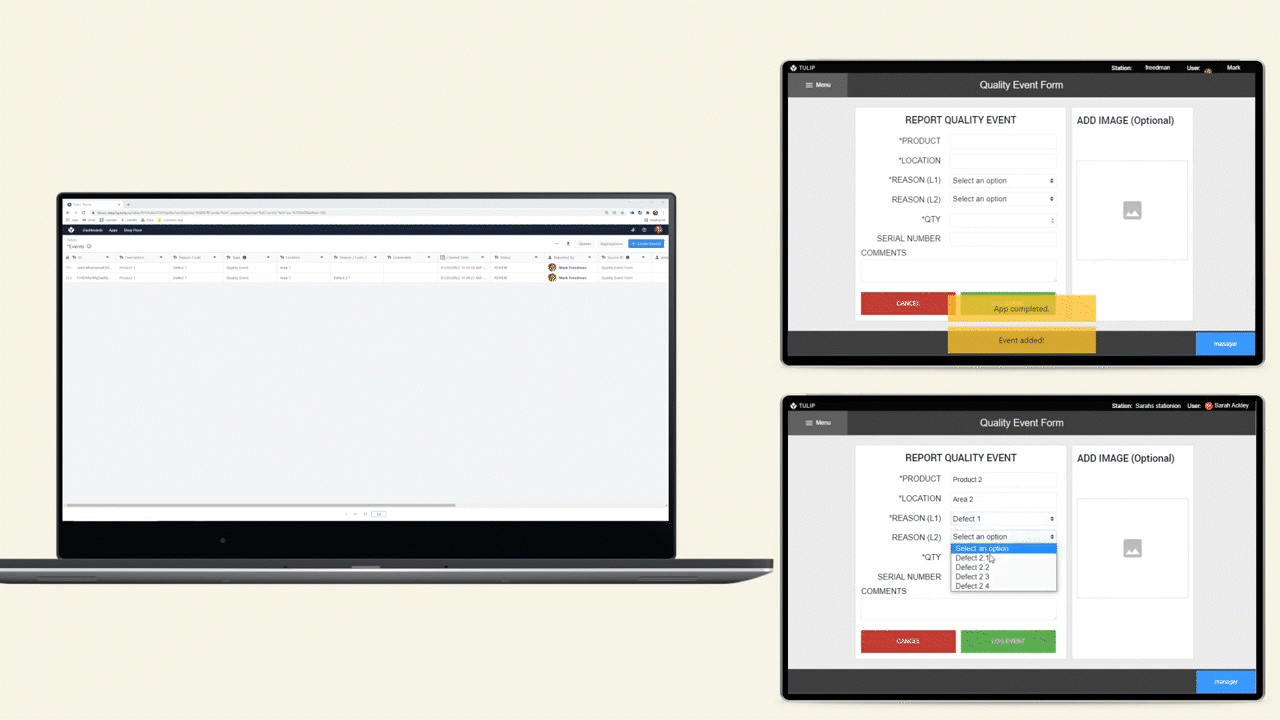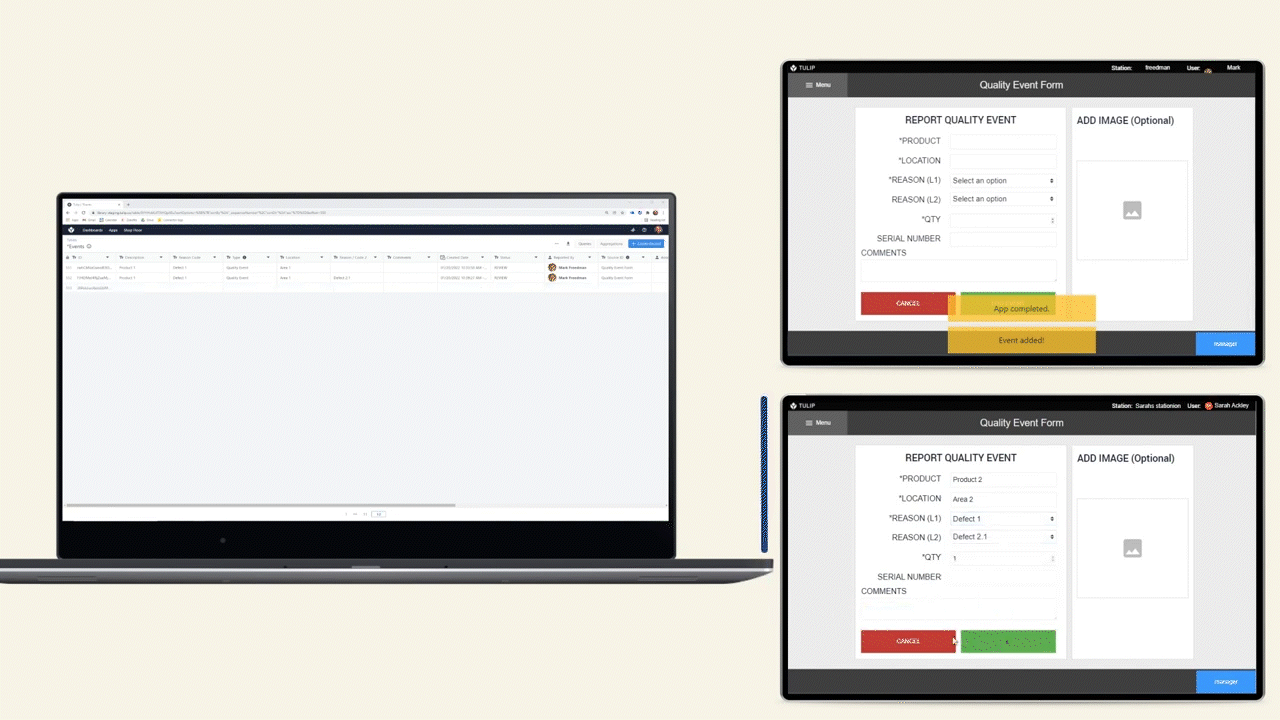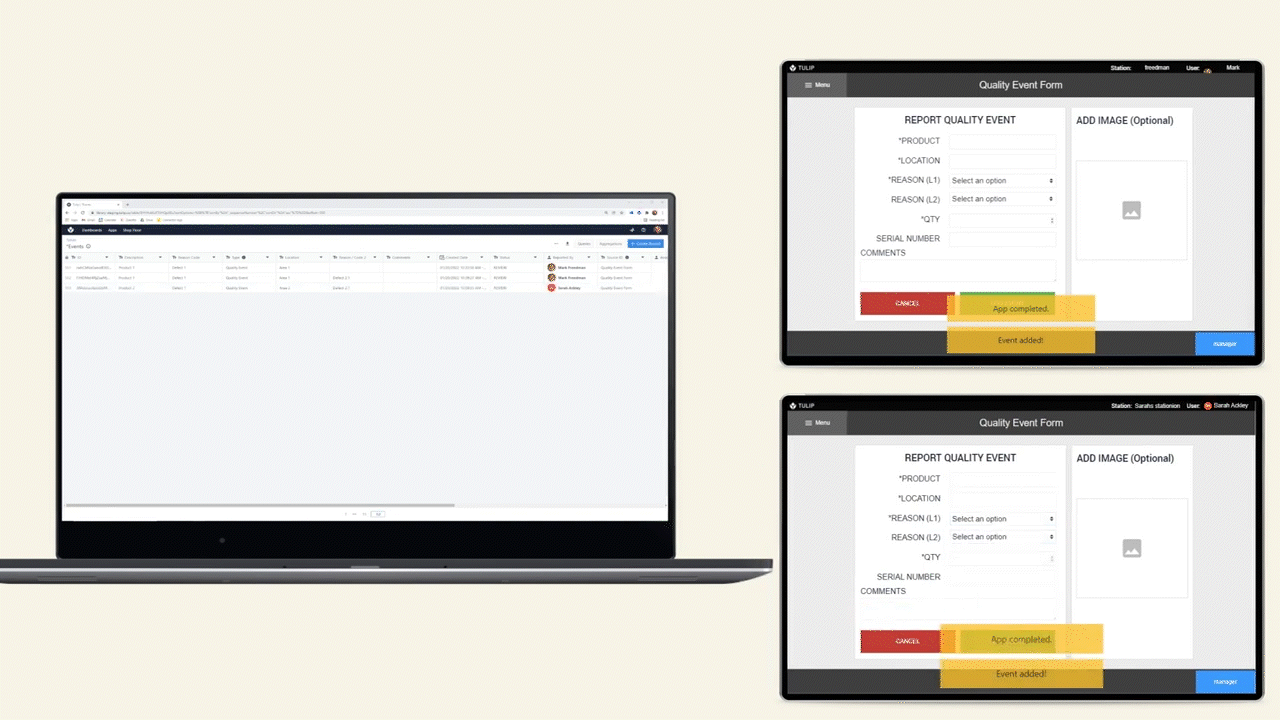
The diagram below shows an operational flow of data throughout a shop floor.
Data Storage Options
There are 2 options for storing data in Tulip, Tables and Completions.
Tables
Tables are a cross between spreadsheets and relational databases that are customizable to however you need to present your data. They are sharable datasources that multiple apps can use.
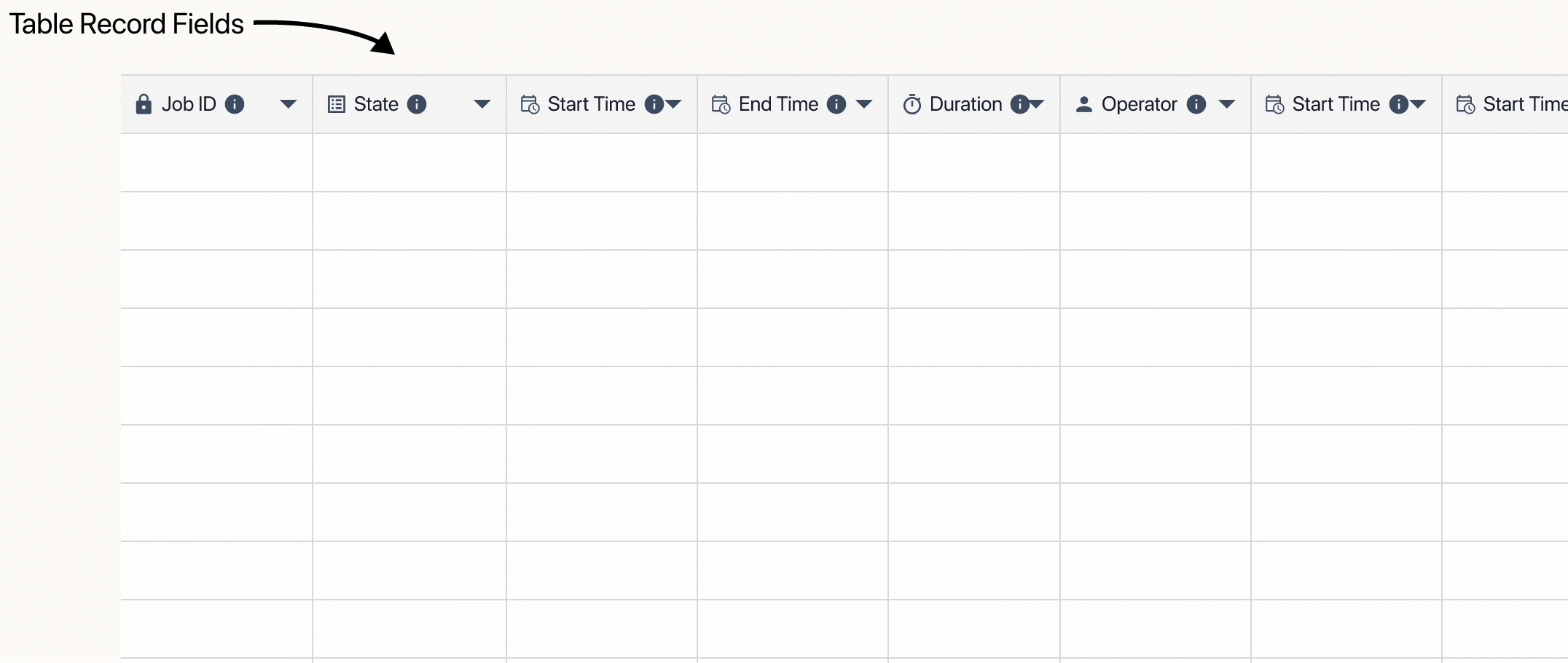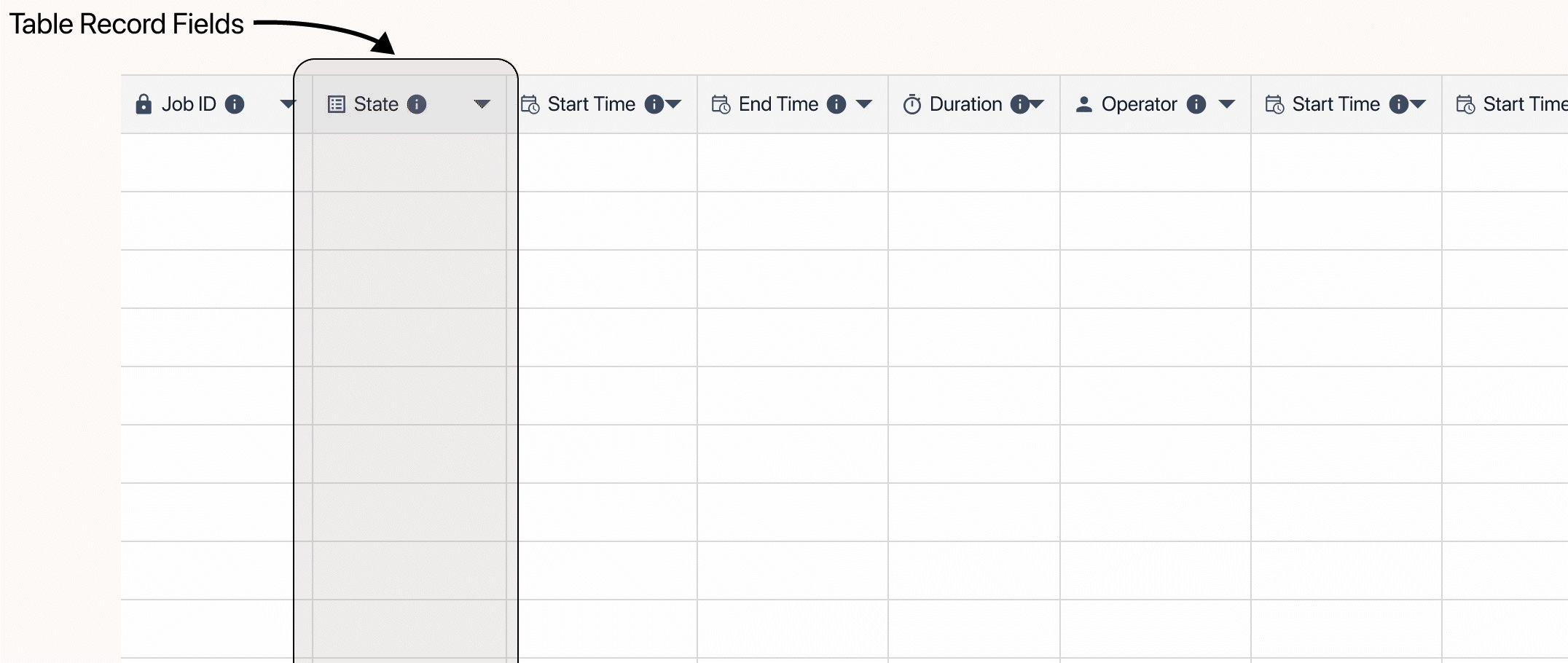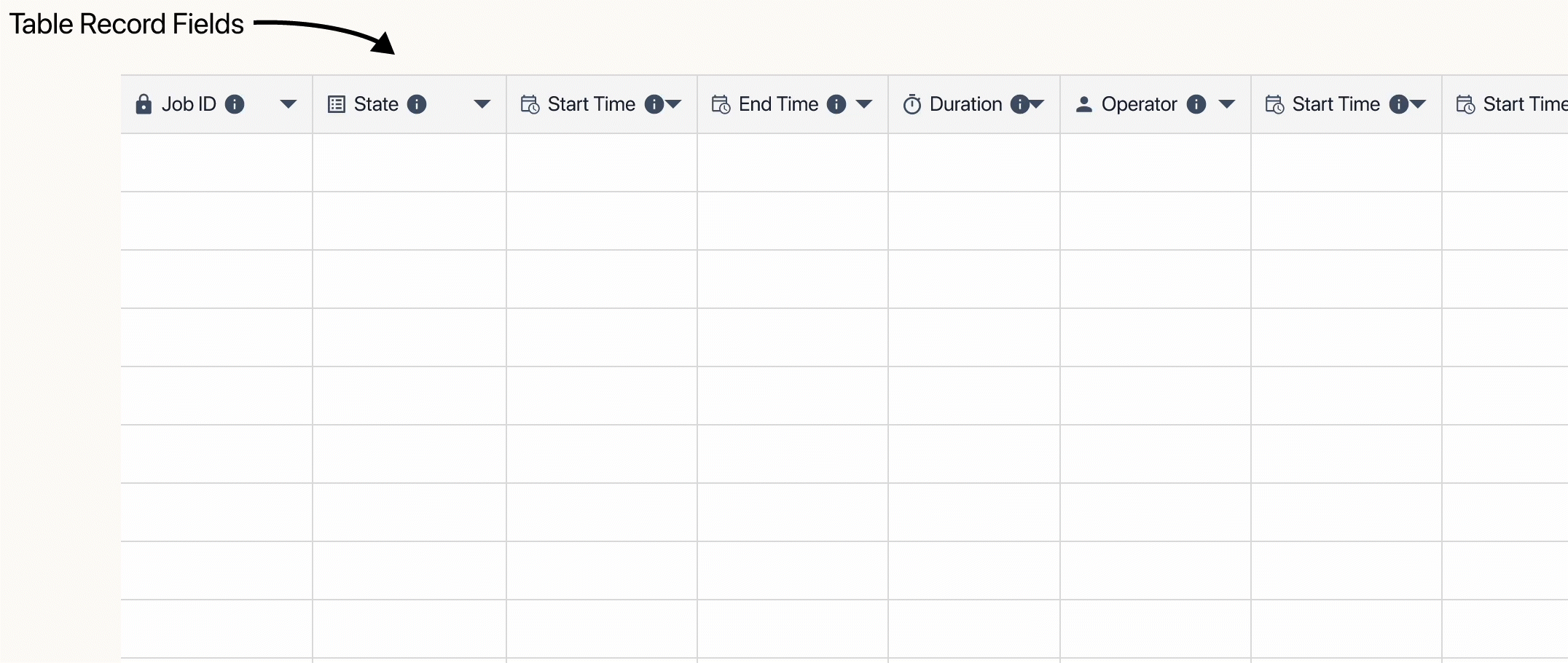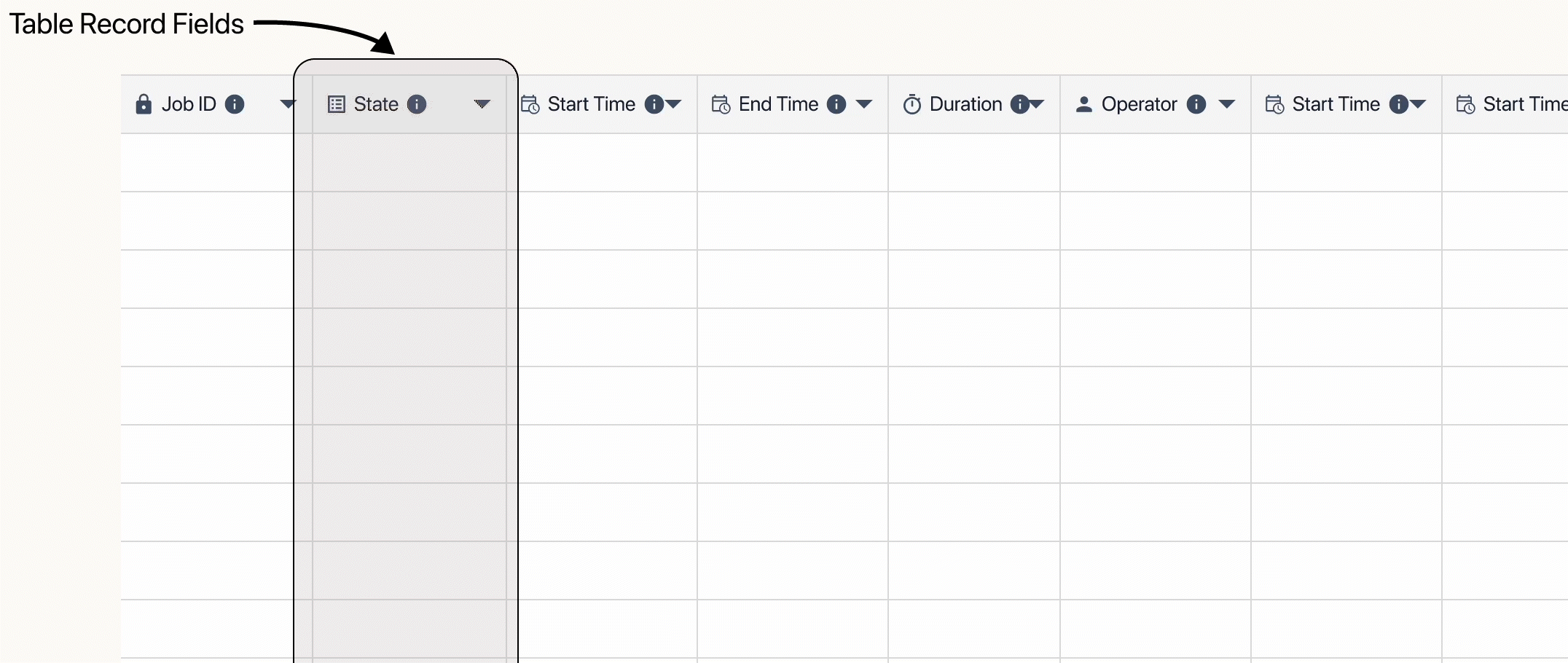
When building a table, you create the Fields which hold and organize the data by records. Fields act as columns, records are the rows of specific data, and each individual piece of data is a Table Record Field.
Tables can be embedded into your app to create, modify, and display records relevant to your tasks.
You can import existing data into Tulip tables, outlined here.
If you don’t want to create your own table, but also don’t have existing data to import, you can use one of Tulip’s preconfigured tables that come loaded on your Instance. These give you an idea of the different fields you can use in tables and general types of data that can be logged. The options for data types include:
- Text
- Integer
- Number
- Boolean
- Datetime
- Interval
- Color
- Image
- Video
- File
- Machine
- Linked Record
Each of these fields will correspond to data inputs used in your application. To view the records in a table, navigate to the table screen via your Tulip instance page. Hover your cursor over “Apps” and select “Tables”.
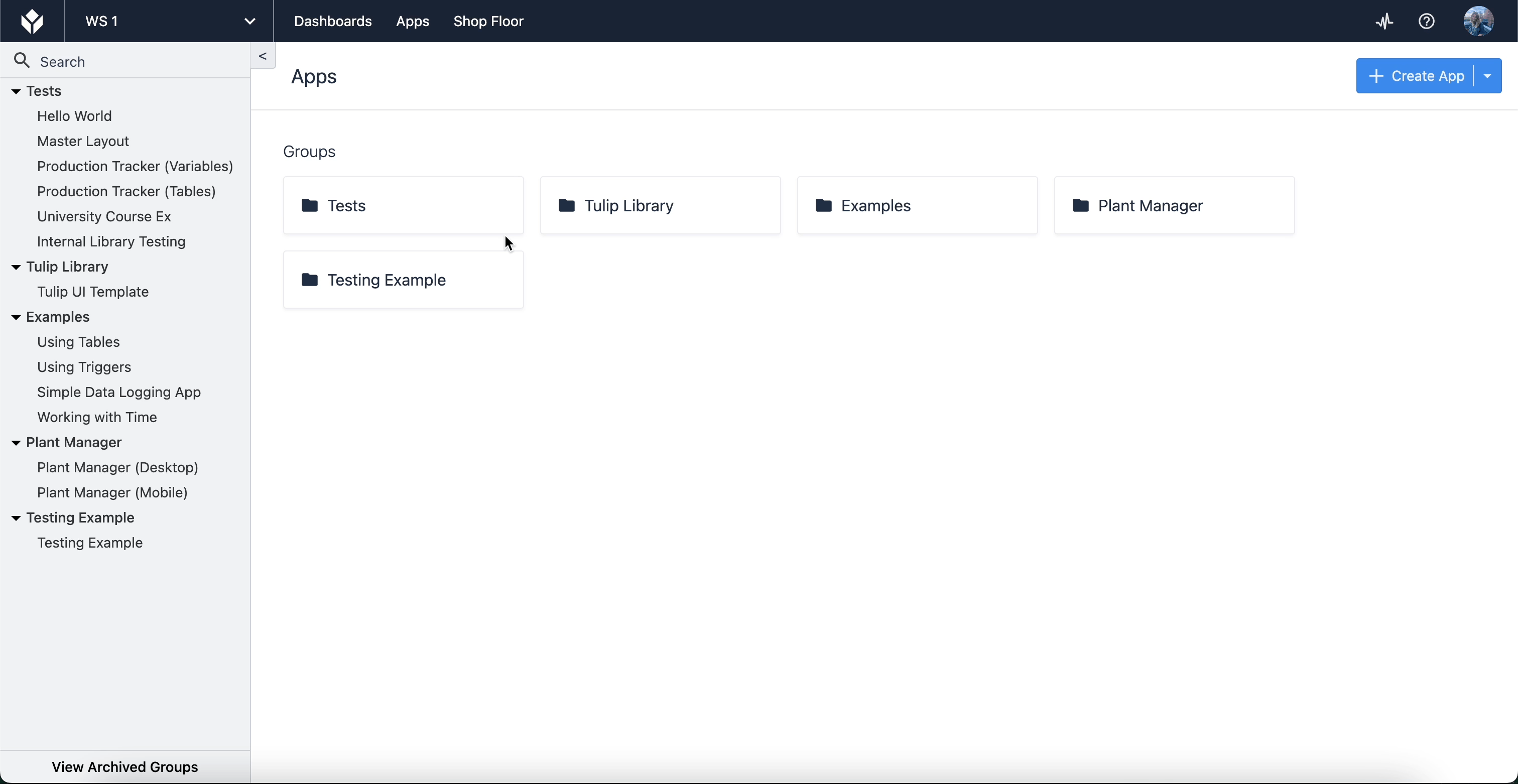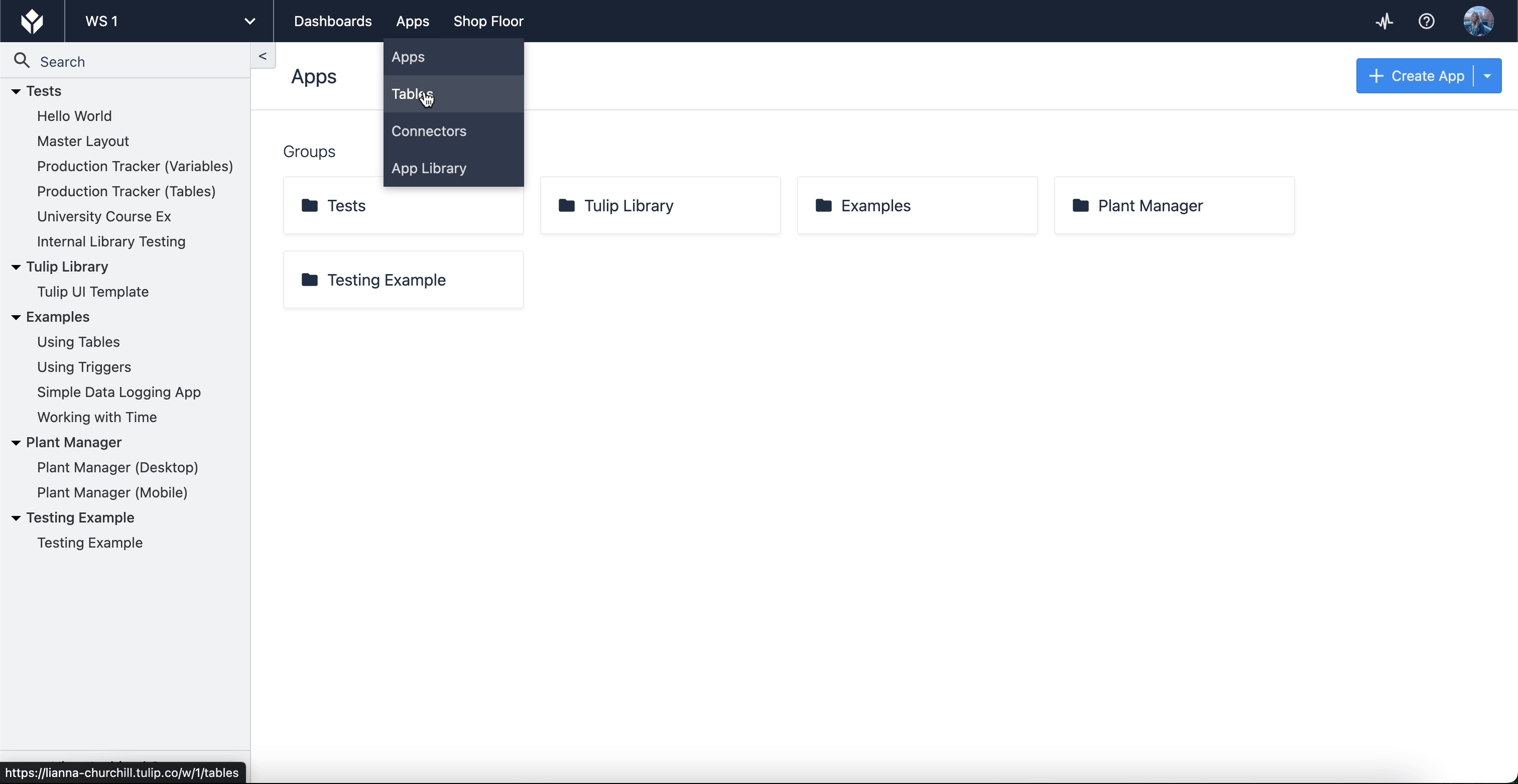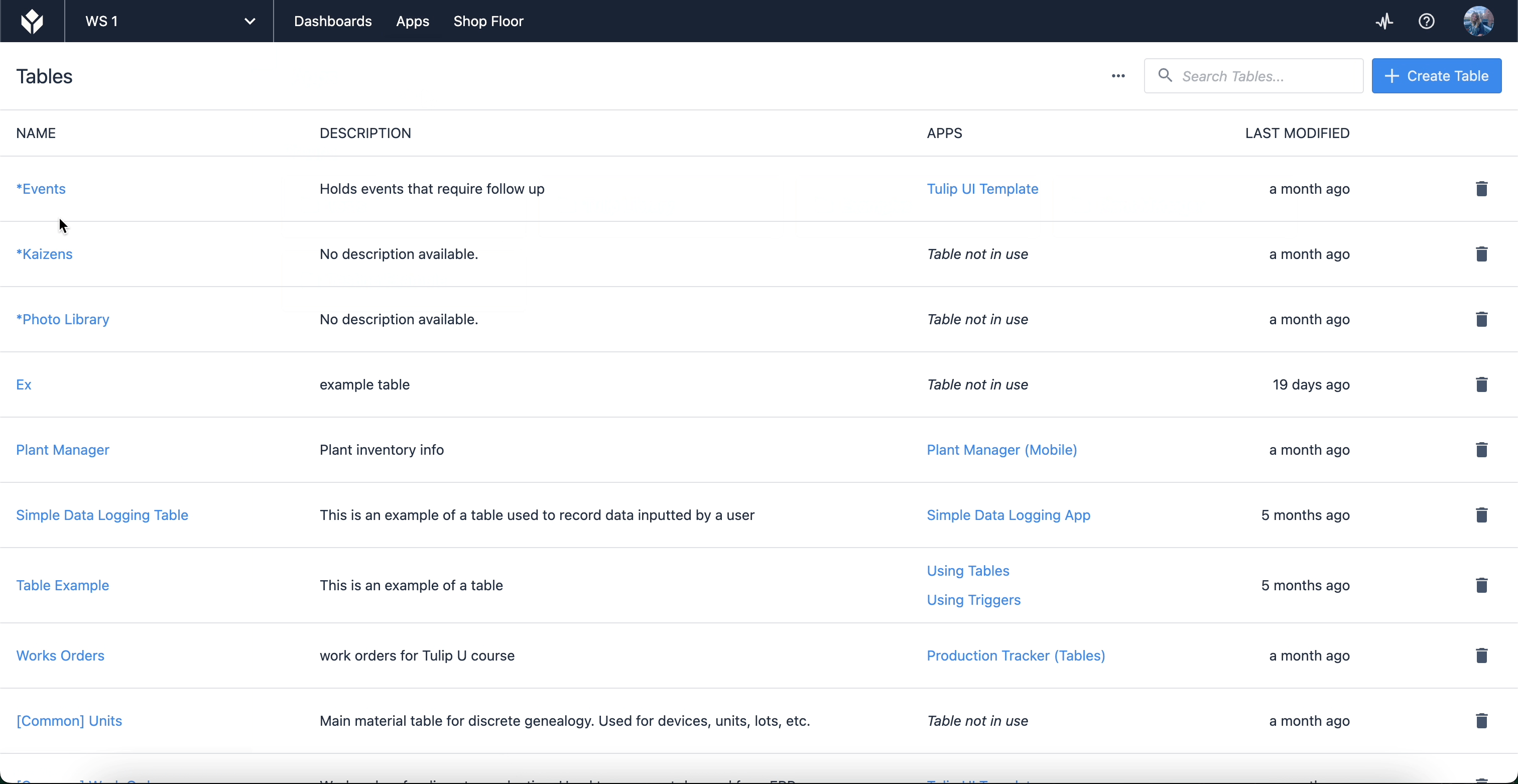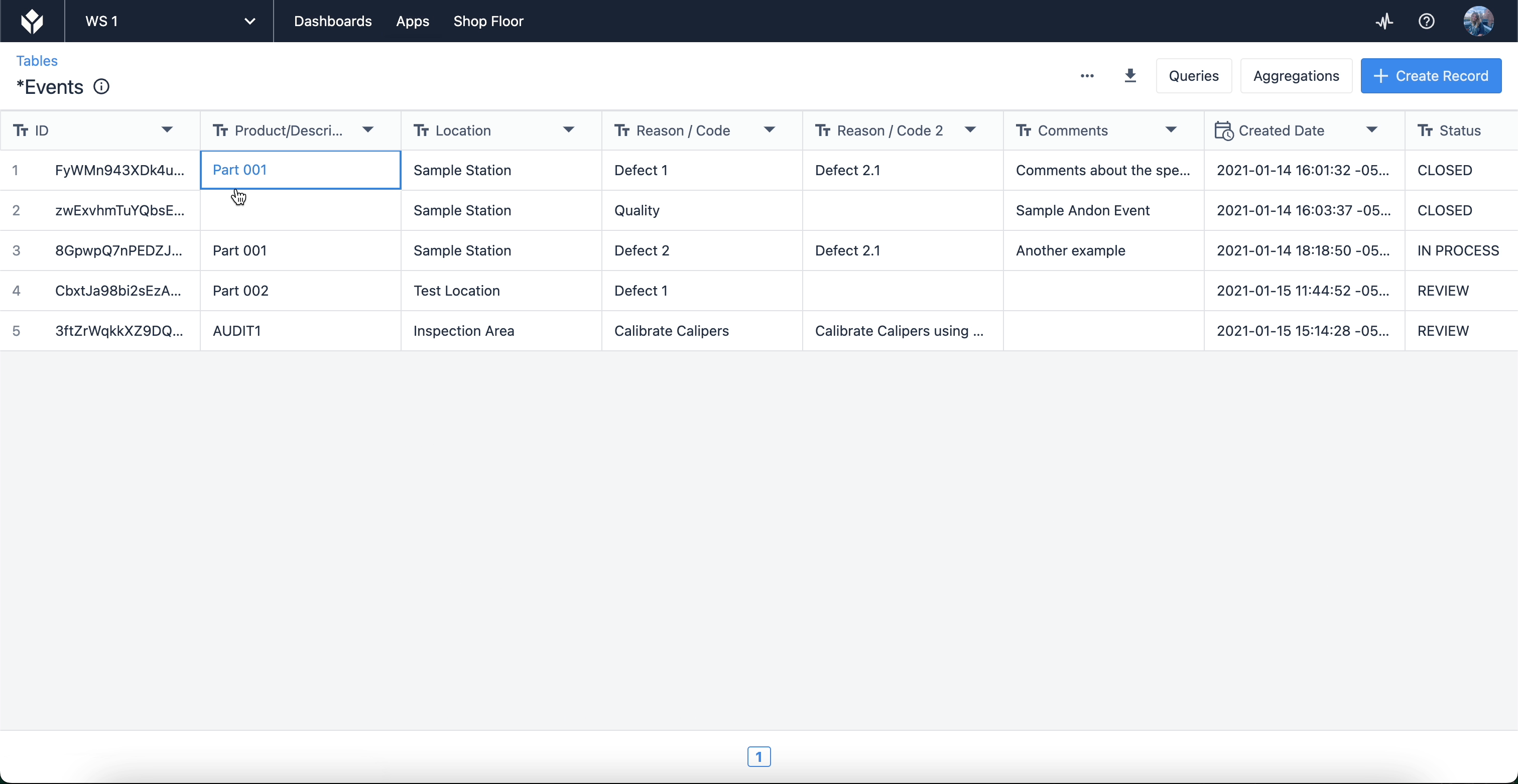
Here, you’ll find a list of tables that you have created or have access to for use in your apps. When you select a table, you’ll be able to edit the fields and records themselves, as well as create Queries and Aggregations which allow you to leverage table data within apps. Tables can also be linked to each other (for use cases like product genealogy).
Recommended Tulip Table Usage
Tulip recommends using Tables to store, at a high-level, two different types of artifacts: physical and operational.
Physical artifacts are tangible objects or components that are used or produced during operations, such as batch/lot or equipment.
Operational artifacts are non-physical elements or components that enable or support operations, such as defect events or kanban configuration.
To learn more about using Tables, see:
Completions
App Completions are ideal for storing and organizing production data. Metadata fields are automatically generated and stored once a user completes or Cancels the app. These fields include:
- App duration
- Start and end time
- Logged-in user
- Station name
- Comments
- App version
- Execution ID
- Canceled (whether or not the app was canceled)
Unlike data stored in Tables, data stored in app Completions cannot be edited. This ensures the information is absolute: unable to be manipulated or changed and an accurate reflection of the app’s utilization.
Completion data can only be used by one app and is also less accessable from outside systems.
To access the app Completion data, select an app from an app group in your Tulip instance. Once at the main screen for the app, select the “Completions” tab.
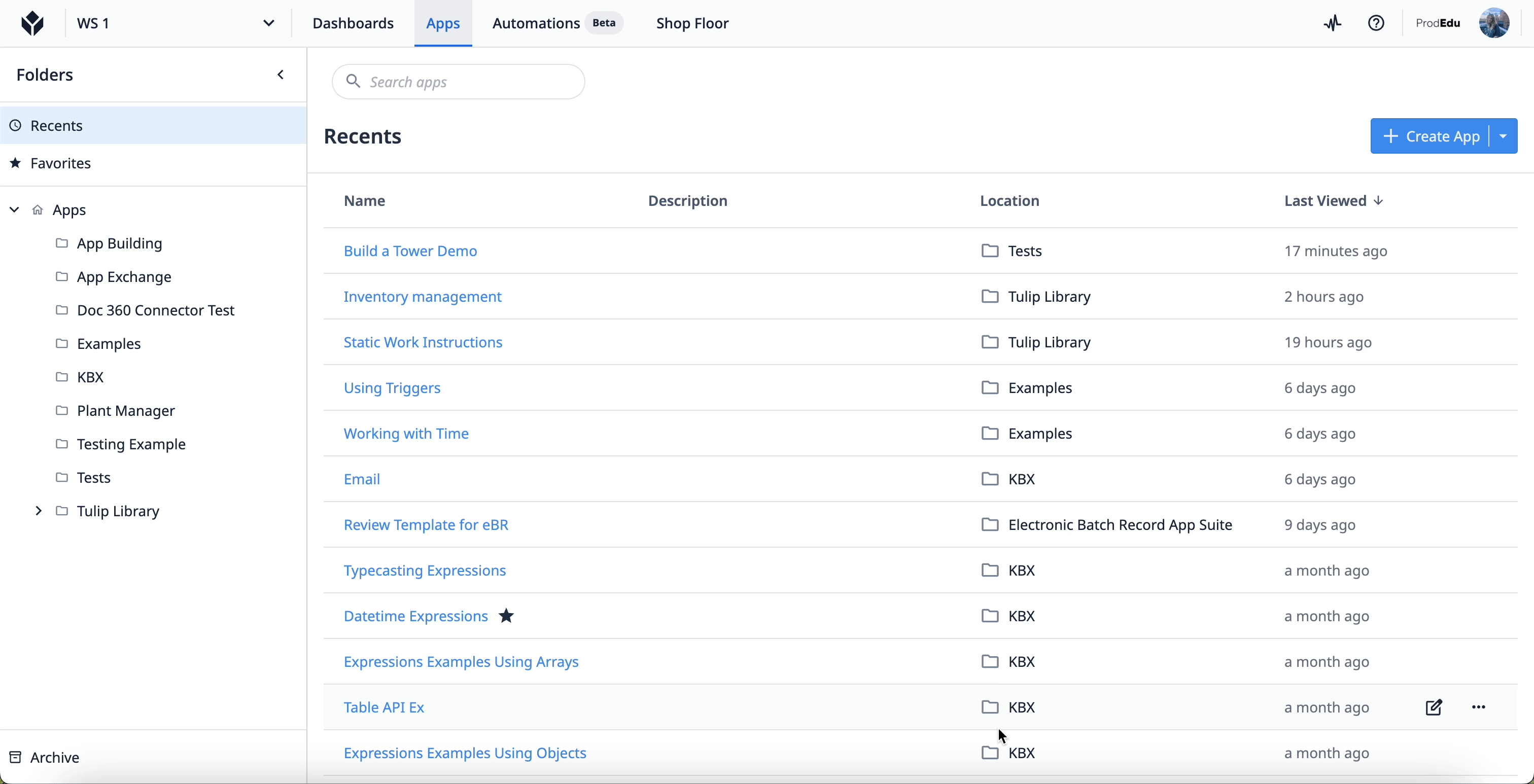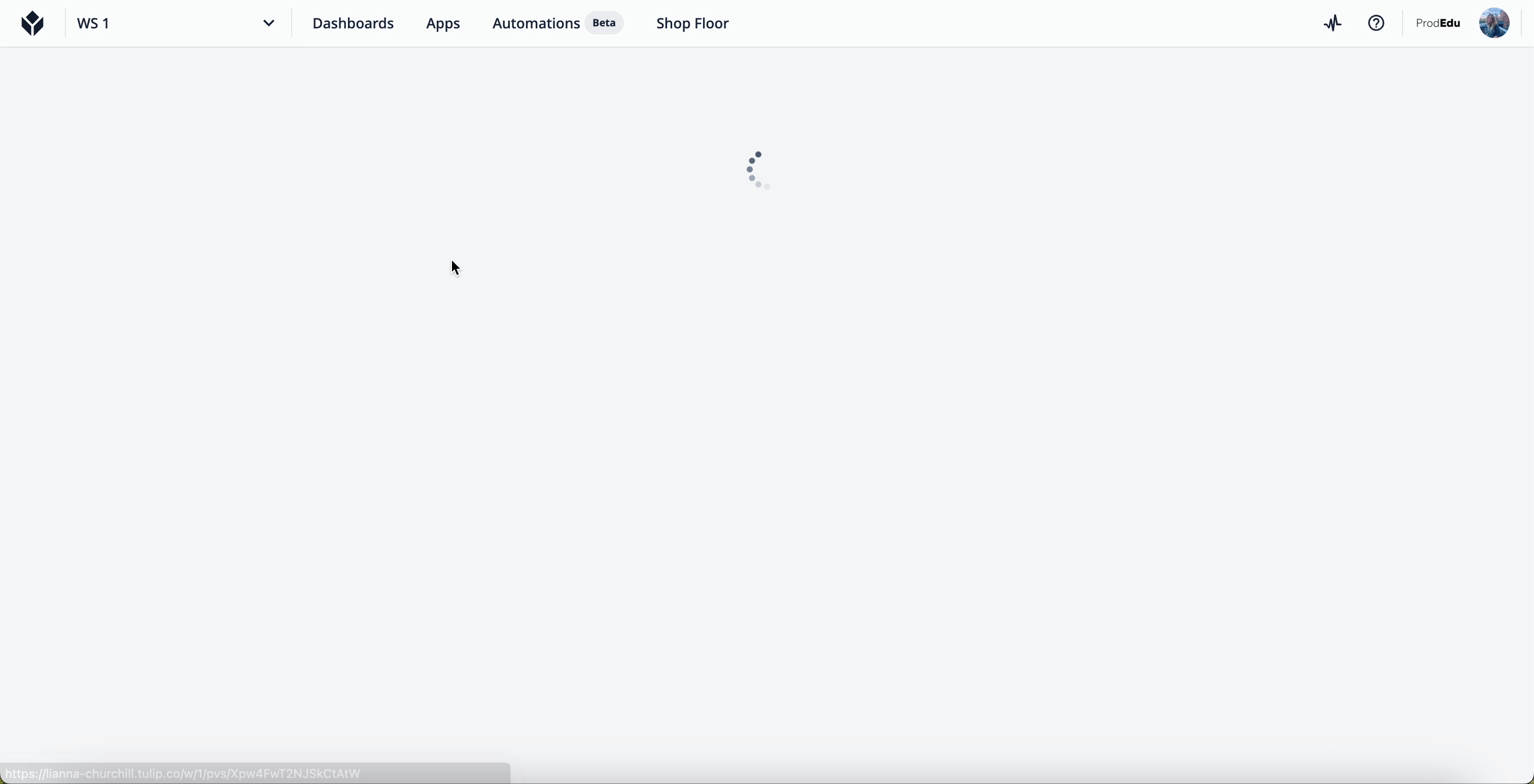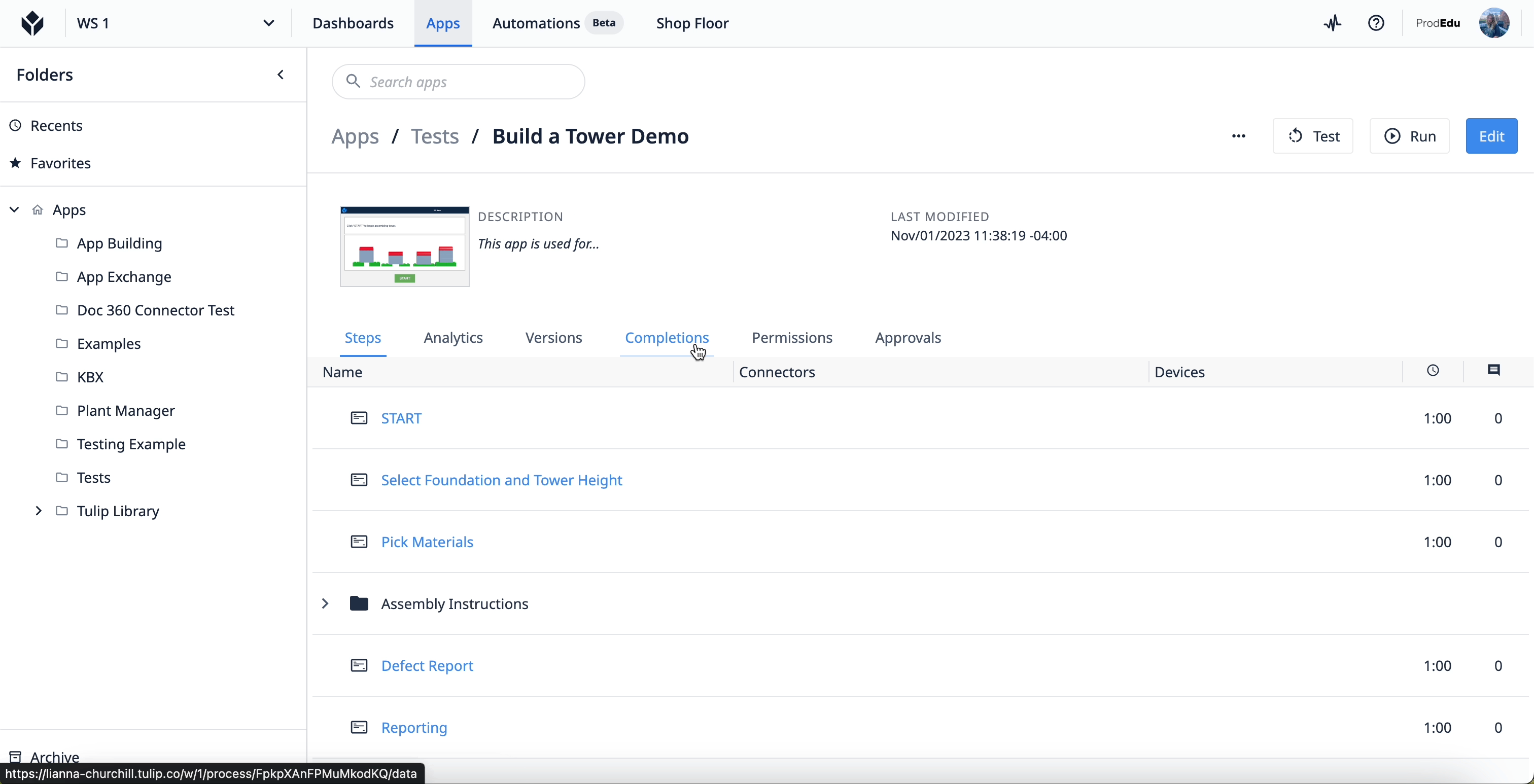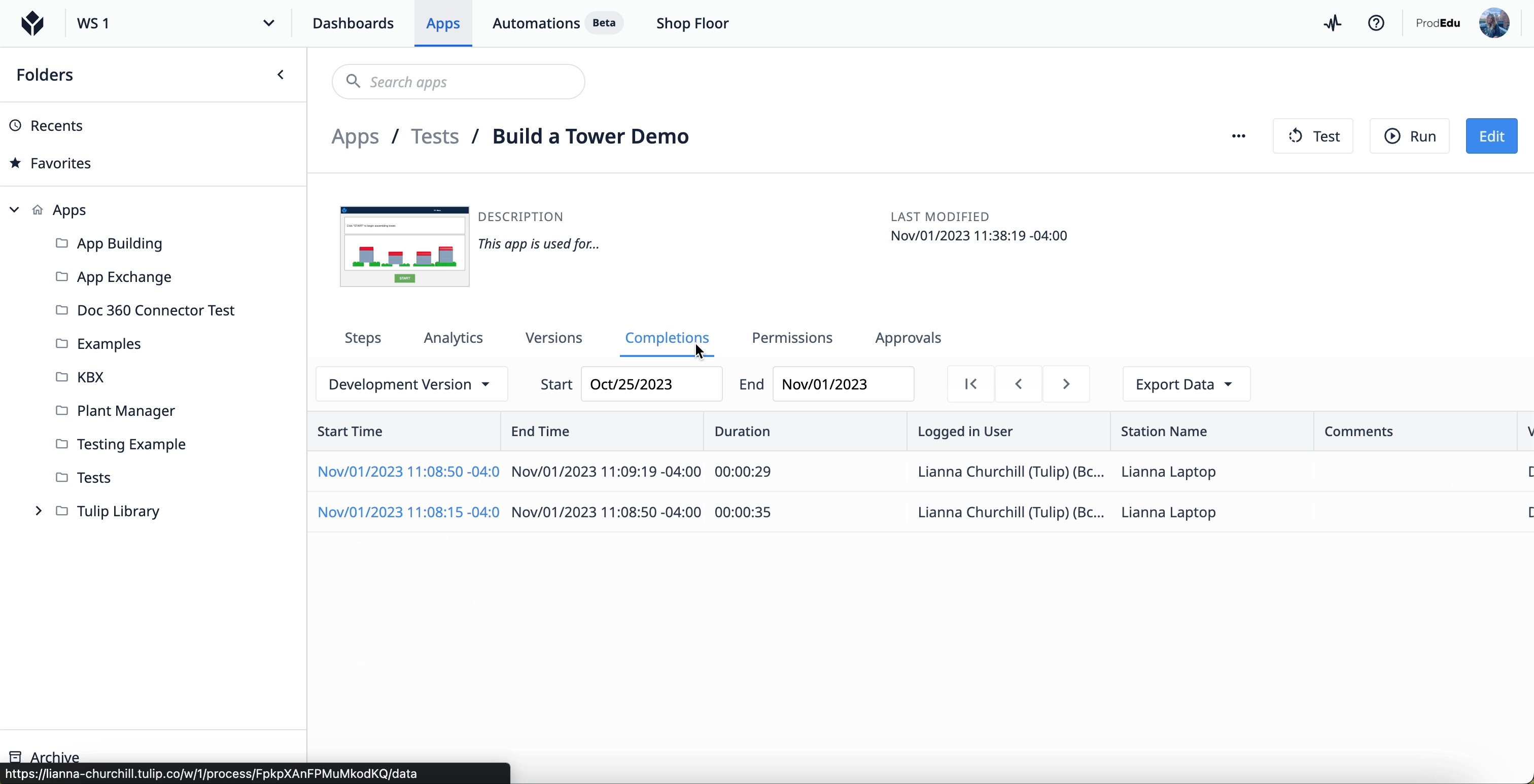
Learn more about completions here.
Tables vs completions
With completions storing automatically to app data, you may wonder when you would want to set up a table for data instead.
Completion data is immutable, whereas the fields within tables are created based on your needs. Table data also writes from your app based on the triggers and variables that you set; however, completion data only writes when a user either completes or cancels the app. While completion data offers ease and instant automation, table data can be made unique to your app and has flexibility to use the data across multiple apps.
Best Practices for Storing Data
Because data storage is customizable for your operations, there are many ways you could set up data structures. Tulip recommends several practices to ensure you build tables and store data with the following goals:
-
Data is easily accessible
-
Data is visible to necessary people and systems
-
Data is centralized and not duplicated elsewhere
Learn more about Tulip’s best practice for storing data here.
Apply a Data model
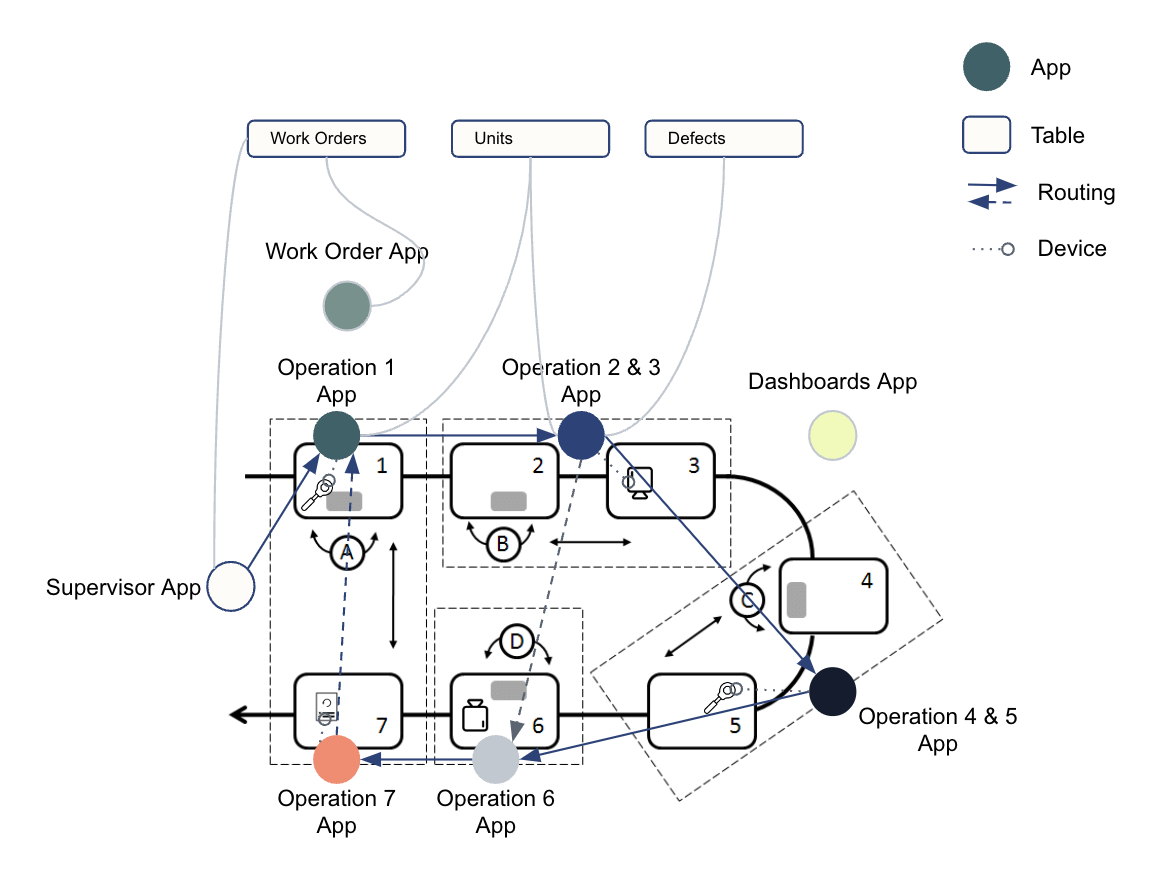
Tulip has a pre-built common data model to suit multiple use cases, so that you can adopt and adapt it to your specific needs:
In Tulip, a common data model is a collection of defined tables that are flexible enough to share data throughout a solution of apps.
The diagrams below illustrate how tables share common data through apps.
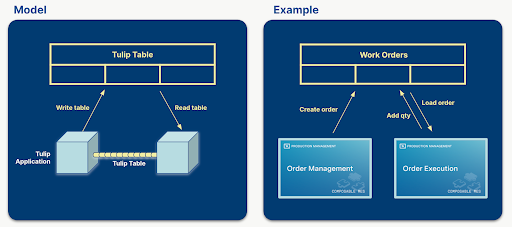
A common data model offers standardized and expandable data schemas, streamlining data handling across systems by representing widely used concepts (i.e. Work Orders, Units). This simplifies the creation, compilation, and analysis of data, and provides a significant opportunity for improved data management.
Tulip Tables should primarily follow the Digital Twin model, meaning tables should reflect the physical plant or shop floor as strictly as possible. Historical app data should be confined to Completion Records to ensure tables are not storing master data or duplicating data from Completion Records or external records.
Learn more about how to use a common data model here.
Take the Common Data Model course on Tulip University here.
Use data in apps
To display, edit, or enter Table data in your apps, you’ll first need to become familiar with Widgets. Input Widgets allow you to edit and enter data that will reflect in your table. Embedded widgets display your information and can be configured so you can interact with your tables. For a full tutorial on incorporating table data, see:
Completion data can be displayed in your apps through Analytics. You’ll first need to create an analysis using your completion data and then embed that analysis into your app.
Learn more about using completion data to create an analysis, see here.
How Tulip Stores Your Data
Because Tulip is a self-serve platform, you can determine which of your data is transmitted and stored. The Tulip Cloud stores your data on AWS, using either a MongoDB or PostgreSQL database. Tulip uploads all images, videos, and PDFs automatically to Amazon’s S3 storage, eliminating the need for you to worry about managing storage or keeping track of your collected data.
Next Steps
Start working with data with guidance from Tulip experts:
- Walkthrough: Build your first table
- Working with Data and Tables University course
- Understanding App Completions and Table University guide
- Integrate with external systems
Did you find what you were looking for?
You can also head to community.tulip.co to post your question or see if others have faced a similar question!


.gif)
.gif)