Learn how to query your Tulip Tables and build aggregations that are accessible within Tulip Apps
In this article, you will learn...
- The capabilities of table queries and aggregations
- How to build queries and aggregations
- How to use queries and aggregations in Apps
Overview
Table Queries and Aggregations enable you to interact with Tables in a dynamic way, filtering and summarizing your data for use in Apps.
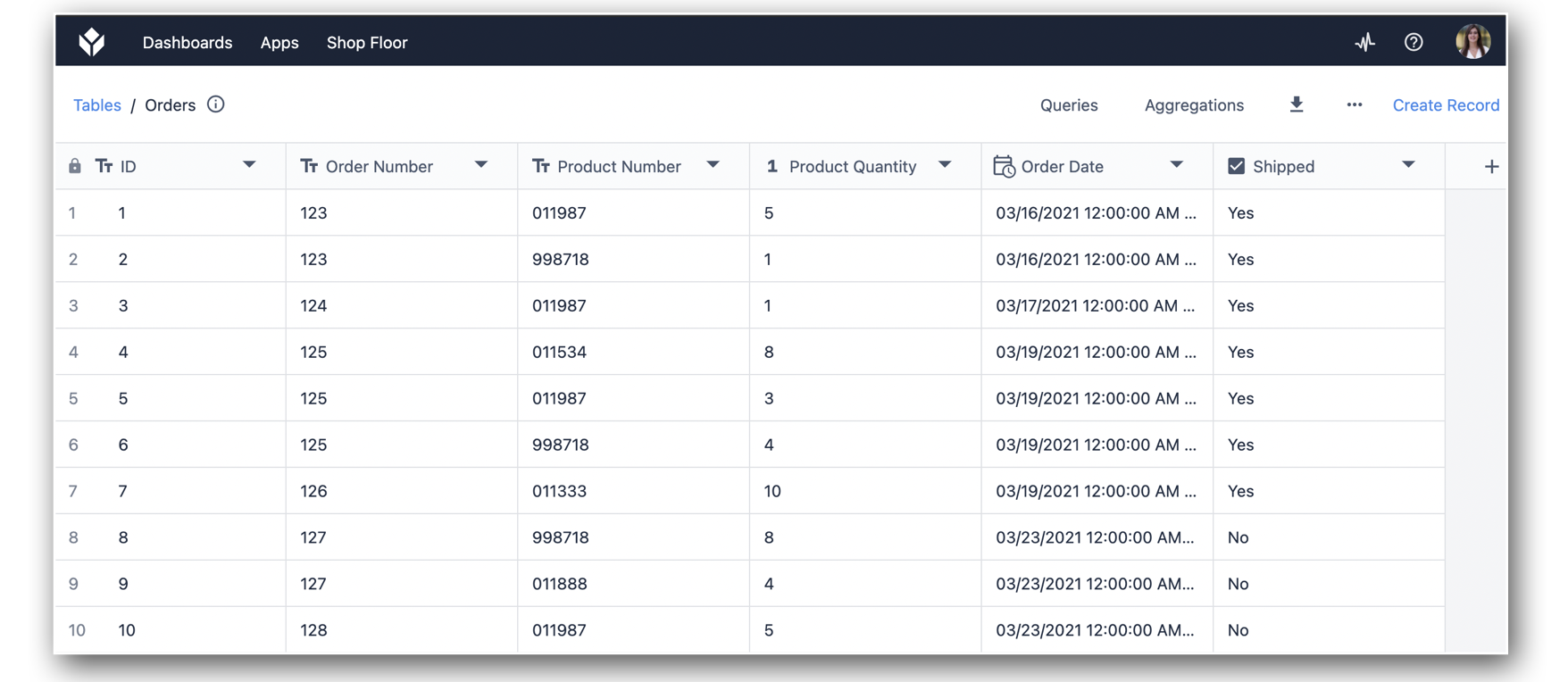
For this article we will be referencing the following Table of Orders, that has 10 rows:
In the top right, you can see the buttons Queries and Aggregations. Click on Queries to add a new query.
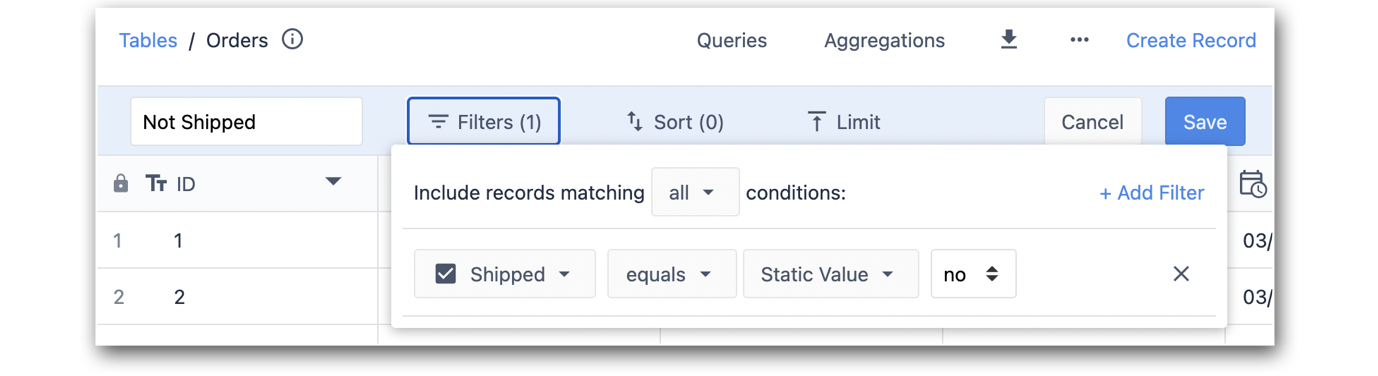
The following example uses a filter to return only records that have not been shipped:
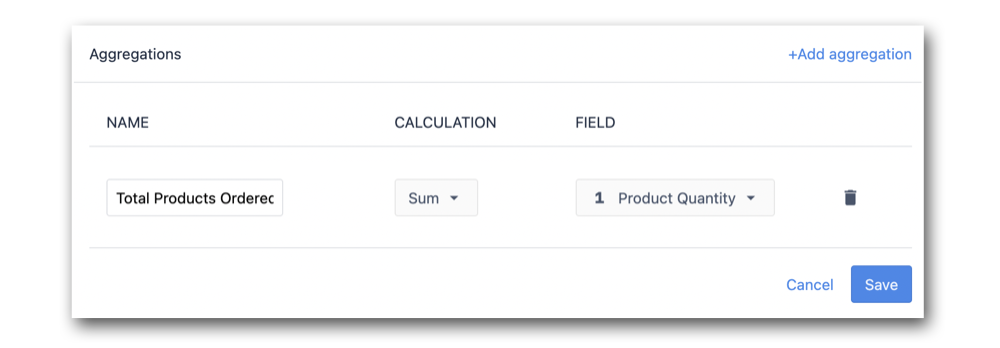
Aggregations are added on top of a query, and are built at the table level like queries. Click on Aggregations to create a new aggregation.
The following example will Sum the table field, Product Quantity:
Queries
A query let's you filter and sort data in a tables. Queries can use either static values or dynamic values based on app input.
Filters
Filter records by comparing a specific column, or multiple columns, to either a Static Value or an App Input.
Examples of comparison options include:
- equals / does not equal
- is null / is not null
- contains / does not contain
- starts with / does not start with
- ends with / does not end with
- is in
- is greater than or equal to / is less than or equal to
- is after or at / is before or at
Static Value will be statically set when building the query, but App Input will be configured in the app itself. The App Input can be configured to be a:
- Variable
- Static Value
- App Info
- Tulip Table Record
You can now use the Created At and Updated At fields in table queries.
Sorting
Customize the display of the records, by configuring the Sort option. Examples include:
- A to Z / Z to A
- 0 to 9 / 9 to 0
Limits
The maximum number of Records returned by a query.
- Default: 1,000
- Maximum: 1,000
If there are more records in your table matching the query filters (or overall if you don't configure any filters) than the limit, only as many as specified by the limit are included in the query result.
If the query includes a sorting, the first records according to this sorting will be included.
Test
After configuring the query by setting the Filter, Sort and Limit options, the query can be tested right on the Table by clicking Test. This will simulate what the query would return in an app.
Use queries in apps
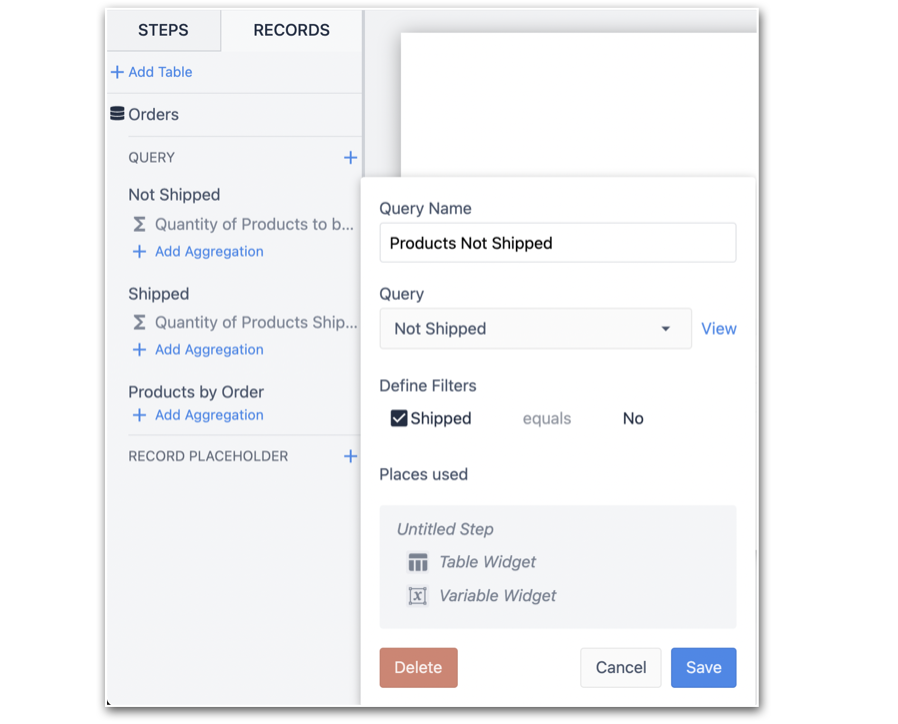
To add a query to an app, first add the table to the App by clicking on the Records Tab, and then +Add Table. Next, click Query.
In the modal that appears, give the query a Query Name, and if applicable, configure the App Input associated with the filter. In this example, see the query Products Not Shipped:
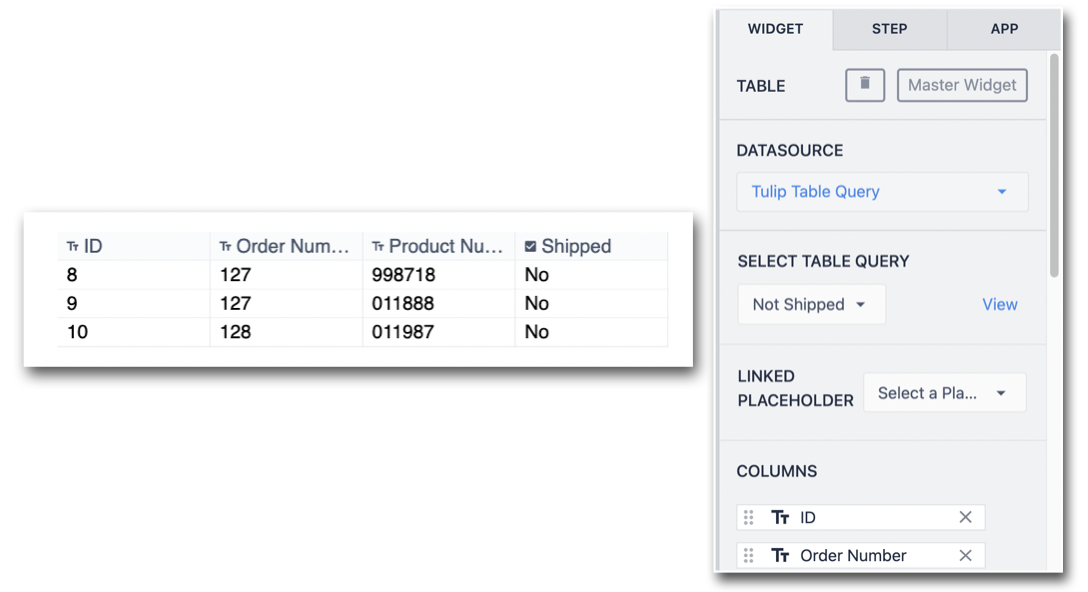
Now that the query is configured in the app, embed an Interactive Table, and select the Datasource to be the query.
The embedded table will display the results of the query. In this example, there are 3 records returned that fulfill the filter, 'Shipped' equals 'No':
Aggregations
Aggregations are summary values that are ran on top of queries, and can calculate one of the following values for a particular column:
- Average
- Count
- Max
- Min
- Mode
- Note: if two values have identical frequency, the lower value will always be returned.
- Sum
- Unique Values
Limits
Aggregations are able to consider a maximum of 1,000 records.
Aggregations are performed on the records returned by the configured query. The limit set for the parent query of an aggregation also applies to the aggregation (1,000 records).
An aggregation may show unexpected results if the table has more records for the given filters than the limit and the user is not aware of the query limit.
If you need to aggregate over more than 1,000 records for use in an app, use the runAggregation endpoint of the Tulip API, which supports up to 100,000 records, via a connector function.
If you only need to visualize an aggregation of more than 1,000 records, build a Single Value analysis with Analytics which allows to aggregate across all records in a table.
Use aggregations in apps
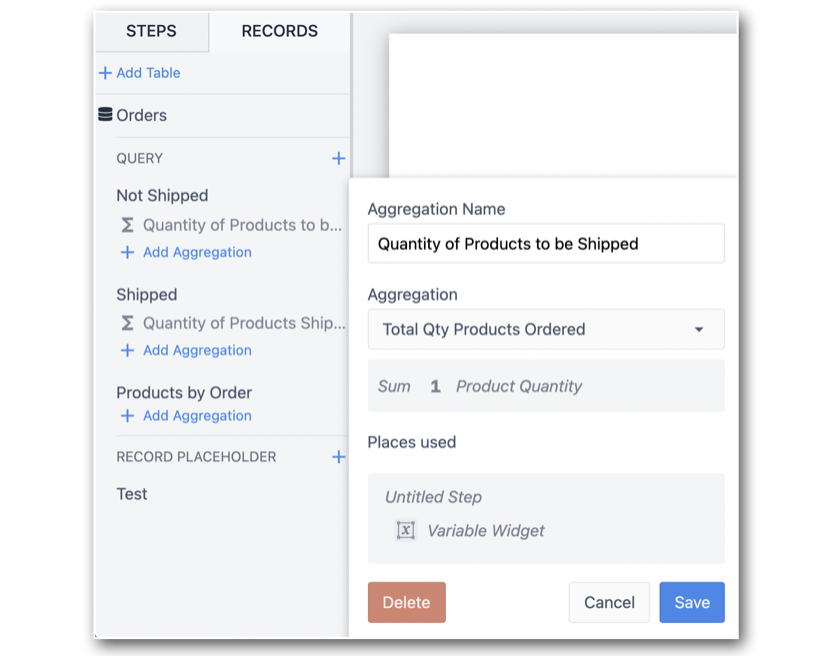
Similar to how a query is added to an App, add an aggregation by clicking +Add Aggregation, and assign an Aggregation Name.
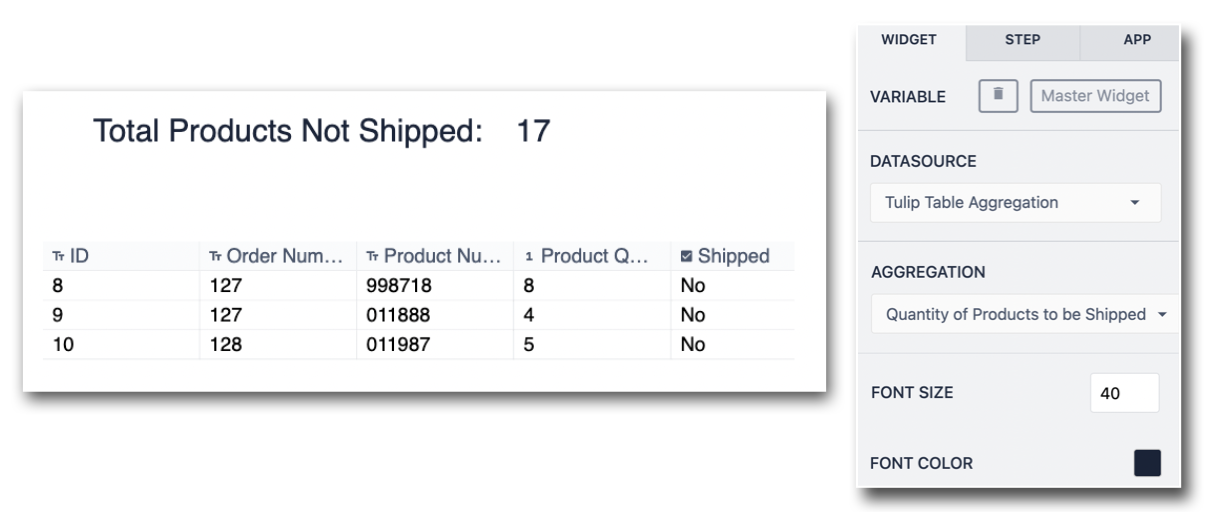
In this example, the aggregation Total Qty Products Ordered is being ran on the query that returns only Records that have not been shipped. For this reason, the Aggregations name is Quantity of Products to be Shipped:
To embed the aggregation in an app, drop a Variable into the app and choose the Datasource - Tulip Table Aggregation. Next, select the Aggregation Name that was configured when adding the aggregation to the app.
In this example, the Aggregation Sum of Product Quantity was ran on top of the Query returning records that need to be shipped. This returns a total of 17:
Use aggregations in app logic
With aggregations, you have the ability to build app logic around an aggregation's value. See an example below:
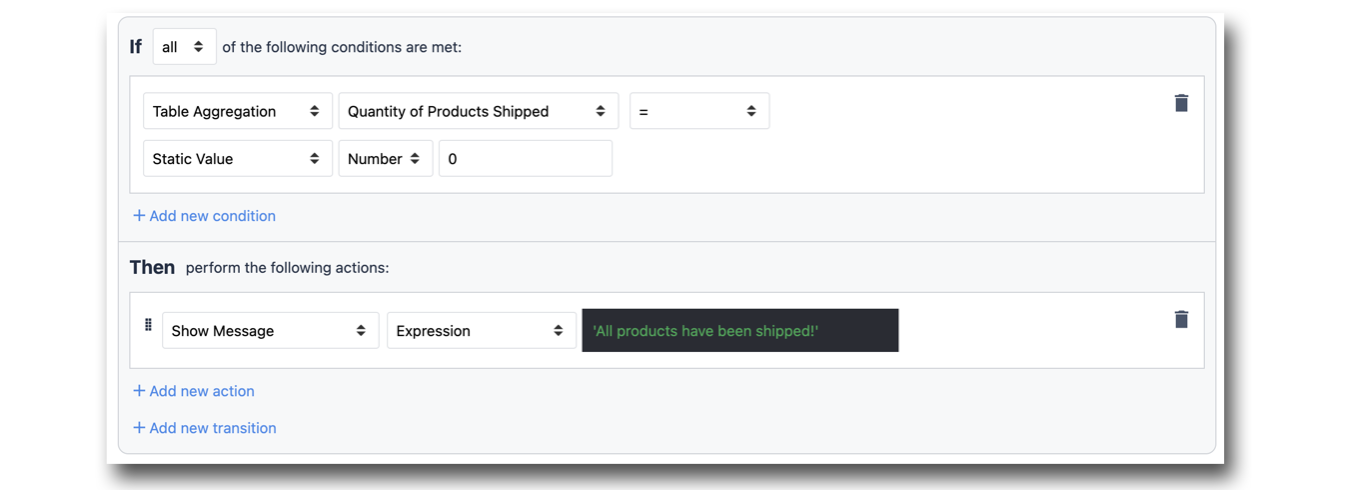
Please note that Single Number Tulip Analytics are not currently accessible from within an app, and can't be directly leveraged with app logic. By running and aggregation off a query, you will be able target this value, and thus build app logic around it.
Did you find what you were looking for?
You can also head to community.tulip.co to post your question or see if others have solved a similar topic!


.gif)