To download the connector, please visit: Library Page
Send data from Tulip to Solace and a number of cloud services via Solace's REST API service
Purpose
This guide provides a high-level starting point for integrating Solace to Tulip. This ultimately provide additional ways to stream information between Tulip and other systems via several methods such as MQTT, REST, AMQP, and more.
Solace is a streaming middleware to simplify a number of integration with an event-driven architecture (real-time, no batches)
Check out their integration resources here
Setup
The following steps are required for integration:
- Solace Account
- Solace Cluster (EKS)
- NOTE: The REST API Credentials will be created with the Solace Cluster
How it works
You can use the Solace REST API on a cluster to write data into Solace via REST API. From there, you can stream it to a number of services via kafka, Solace messaging, MQTT, AMQP, and more.
Find the REST API Credentials under "Connect" in a Cluster
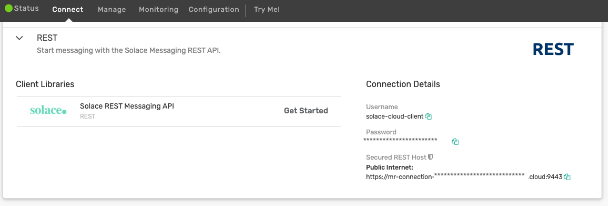
Detailed Tulip Setup
- Update cluster url with the cluster url created in Solace
- Update username and password based upon the information in the connect tab (See REST API section)
- The request body (Plain Text) can be modified to take inputs from a function; the static text is there for example purposes only
Test Solace Subscribe
Go to "Try Me" on the Solace Cluster to subscribe to a topic and view messages
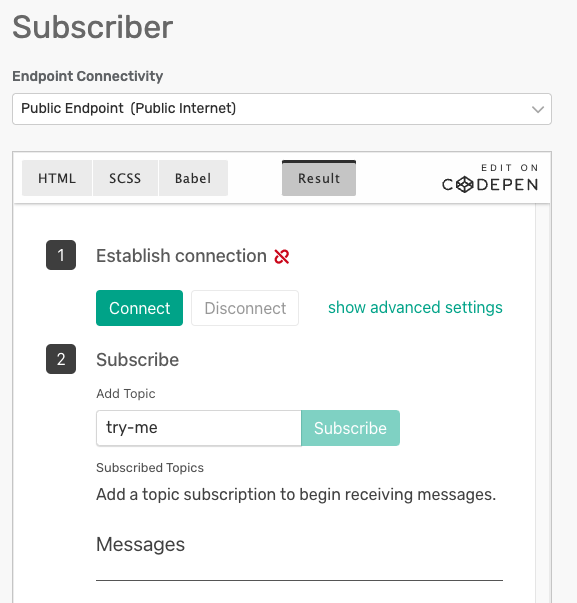
Once you have the Solace Connector, there are several use cases to create value
Use Cases
Stream data from Tulip to AWS, Azure, GCP via Solace
Use Solace to write data from Tulip to Solace via REST API and then have Solace stream it to a variety of cloud resources such as AWS Kinesis, Azure Datalake, and more.
View all their connectors here
Manage system integrations via Solace middleware instead of connecting directly with Tulip
Manage ERP, PLM, CRM, and other integrations via Solace's event-driven architecture to simplify complex integrations.
Next Steps
- Explore more integration opportunities with Solace such as Boomi and more
- Learn more about unified namespace (UNS) and event-driven architectures here