To download the app, visit: Library
Das Quality Management Dashboard ist ein Teil der komponierbaren MES Quality Management App Suite von Tulip. Sie können es einzeln oder in Kombination mit anderen Anwendungen verwenden.
Zu den Hauptaufgaben der Anwendung gehört die Bereitstellung von einfachen Analysen für die Benutzer und die Möglichkeit, Besonderheiten in Bezug auf Produkte, Chargen oder Fehler zu untersuchen. Dadurch wird der Prozess der Qualitätsanalyse vereinfacht.
Nutzung und Wertschöpfung
- Sichtbarkeit: Ein Qualitäts-Dashboard bietet eine zentrale und visuelle Darstellung der wichtigsten Qualitätsmetriken und Leistungsindikatoren. Es bietet den Beteiligten, einschließlich der Geschäftsleitung und den Mitarbeitern an der Front, einen klaren und unmittelbaren Überblick über den Qualitätsstatus des Unternehmens, Trends und Bereiche, die Aufmerksamkeit erfordern.
- Kontinuierliche Verbesserung: Qualitäts-Dashboards erleichtern kontinuierliche Verbesserungsbemühungen, indem sie Einblicke in die Qualitätsleistung im Zeitverlauf geben. Durch die Verfolgung von Trends und den Vergleich historischer Daten können Unternehmen verbesserungswürdige Bereiche identifizieren, Ziele festlegen und den Fortschritt bei der Erreichung von Qualitätszielen messen.
- Optimierung der Ressourcen: Durch die Identifizierung der Ursachen von Qualitätsproblemen und Ineffizienzen helfen Qualitäts-Dashboards Unternehmen bei der Optimierung von Ressourcen, einschließlich Personal, Material und Ausrüstung. Durch die Behebung der zugrunde liegenden Probleme können Unternehmen Verschwendung reduzieren, die Produktivität steigern und Kosten senken.
In der Anwendung verwendete Tulip-Tabellen
Alle Anwendungen in der Composable MES App Suite verwenden gemeinsame Tabellen.
Diese Anwendung verwendet vier Tabellen für die Datenanalyse. Grundlegende Analysen basieren auf der Tabelle "Defekte", die es dem Benutzer ermöglicht, die Dauer der Defekte, die Gründe für die Defekte in einem Pareto-Diagramm und die Anzahl der geöffneten und geschlossenen Ereignisse in einem bestimmten Zeitraum zu beobachten. Die Benutzer können auch die durchschnittliche Dauer eines Ereignisses und die Anzahl der innerhalb eines vordefinierten Zeitraums aufgetretenen Fehler abrufen.
Für eine detailliertere Analyse verwendet die App die Tabellen "Arbeitsaufträge " und " Chargen". Die Benutzer können einen bestimmten Arbeitsauftrag oder eine Charge auswählen, um alle zugehörigen Fehler, kategorisiert nach Typ, anzuzeigen. Außerdem können sie alle zugehörigen Messungen einsehen, die in der Tabelle Inspektionsergebnisse aufgezeichnet wurden.
(Operatives Artefakt) Arbeitsaufträge
- ID: Eindeutige Kennung des Arbeitsauftrags
- Bediener: Bediener, der den Arbeitsauftrag ausgeführt hat
- Übergeordnete Auftrags-ID: Verweis auf einen übergeordneten Arbeitsauftrag (zum Beispiel, wenn ein Arbeitsauftrag in mehrere Arbeitsaufträge aufgeteilt werden muss)
- Materialdefinitions-ID: Die Teilenummer des Arbeitsauftrags
- Status: ERSTELLT, FREIGEGEBEN, BESTÜCKT, IN ARBEIT, ABGESCHLOSSEN, VERBRAUCHT, GELIEFERT
- Ort: Dies ist der physische Ort, an dem der Arbeitsauftrag existiert. Es kann eine Stations-ID, eine Orts-ID oder eine beliebige Angabe eines Ortes sein.
- QTY erforderlich: Menge der Teile, die hergestellt werden müssen
- QTY abgeschlossen: Tatsächliche produzierte Menge
- QTY Verschrottet: Die Anzahl der Einheiten, die im Zusammenhang mit diesem Arbeitsauftrag verschrottet wurden
- Fälligkeitsdatum: Das Datum, an dem der Arbeitsauftrag fällig ist
- Startdatum: Aktueller Zeitstempel des Startdatums für den Arbeitsauftrag
- Abschlussdatum: Das tatsächliche Abschlussdatum/die tatsächliche Abschlusszeit für den Arbeitsauftrag
- Kunden-ID: Die Identität des Unternehmens oder der Einrichtung, für die der aktuelle Produktionsbedarf erfüllt wird
(Physisches Artefakt) Einheiten
- ID: Eindeutiger Bezeichner des Einheitendatensatzes, z. B. Seriennummer oder Chargennummer
- Materialdefinitions-ID: Das Teil der Einheit
- Materialdefinition Typ: Die Art des Teils
- Status: z. B. IN BETRIEB oder VERFÜGBAR oder NICHT VERFÜGBAR
- Standort: Der physische Standort in der Werkstatt oder im Inventar. Es kann sich um eine Stations-ID, eine Standort-ID oder eine beliebige Angabe eines Standorts (Bereich, Zelle, Einheit usw.) handeln.
- ANZAHL: Menge der Einheit
- Unit of Measure: Maßeinheit
- Arbeitsauftrag-ID: Der zugehörige Arbeitsauftrag
- Datum der Fertigstellung: Die Zeit, zu der die Einheit fertiggestellt wurde
- Produziert von: Der Bediener, von dem die Einheit fertiggestellt wurde
- ID der übergeordneten Einheit
(Operatives Artefakt) Defekte
- ID: Eindeutiger Bezeichner des Fehlerdatensatzes
- Materialdefinitions-ID: Die Teilenummer oder Materialdefinitions-ID des defekten Teils
- Material-ID: ID des fehlerhaften Materials
- Grund: Unterstützt die Weiterleitung an den richtigen Eigentümer und eine schnelle Lösung. Unterstützt außerdem die Analyse der Fehlerursache.
- Ort: Dies ist der physische Ort, an dem der Fehler entdeckt wurde. Dabei kann es sich um eine Stations-ID, eine Standort-ID oder eine beliebige Angabe eines Ortes (Bereich, Zelle, Einheit usw.) handeln.
- Schweregrad: Auswirkung des Fehlers auf unseren Prozess (kritisch, hoch, mittel, gering)
- Status: Aktueller Status des Fehlers. "Neu", "In Prüfung" und "Geschlossen".
- Arbeitsauftrag-ID: Falls zutreffend, die Work Order ID, auf die sich der Fehler bezieht
- Einheit-ID: Falls zutreffend, die ID der zugehörigen Materialeinheit
- Kommentare: Freier Text zur Erfassung von Kommentaren zu dem Fehler. Kann zur Unterstützung der historischen und ursächlichen Analyse verwendet werden.
- Foto: Für die Aufzeichnung kann ein relevantes Foto aufgenommen werden, das sowohl bei der ersten Lösung als auch bei der späteren Analyse hilft.
- Menge: Die Menge der fehlerhaften Teile/Materialien
- Berichtet von: Benutzer, der das Ereignis protokolliert, in der Regel über den angemeldeten Benutzer der App
- Anordnung: Maßnahme, die zur Behebung des Fehlers ergriffen wurde
- Disposition Zugeordneter: Benutzer, dem die Aufgabe zugewiesen wurde / der den nächsten Schritt bei der Fehleruntersuchung unternimmt. In der Regel ist dies der Qualitätsverantwortliche oder der Vorgesetzte, sollte aber vom App-Ersteller definiert werden.
- ispositioniert Datum
- Abgeschlossen
Inspektionsergebnisse
- ID: Eindeutige Kennung des Inspektionsergebnisdatensatzes
- Arbeitsauftrag-ID: Der zugehörige Arbeitsauftrag, falls zutreffend
- Einheiten-ID: Das zugehörige physische Material
- Materialdefinitions-ID: Die zugehörige Teilenummer
- Typ: Weitere Kategorisierung oder Klassifizierung der Gruppierung oder des Typs des Ergebnisses
- Status: Verfolgung des Status dieser Prüfanforderung
- Verfahren: Verfahrens-ID für die Inspektion
- Ort: Ort, an dem die Inspektion durchgeführt wurde
- Foto: wenn das Ergebnis ein Bild enthält
- Bestanden: Angabe des Inspektionsergebnisses: Bestanden/Nicht bestanden
- Bediener: Bediener, der die Inspektion durchgeführt hat
- Text-Wert: Erfasster Textwert
- Gemessen: Gemessener Istwert
- Ziel: Gewünschter Zielwert
- LSL: Untere Grenze
- USL: Oberer Grenzwert
Konfiguration und Anpassung
In-App-Hilfe
Wie alle Anwendungen in der Composable MES App Suite enthält auch die Quality Management Dashboard App eine In-App-Hilfe. Dabei handelt es sich um kurze Beschreibungen der erforderlichen Einrichtungsschritte und Tipps für den App-Builder zur Unterstützung weiterer Anpassungen. Lesen Sie diese Anweisungen nach dem Herunterladen der App unbedingt durch und löschen Sie sie anschließend, bevor Sie die Anwendung ausführen.
Tabellen, die Dateneingaben liefern
Diese Anwendung benötigt Informationen aus diesen Tabellen, um richtig zu funktionieren. Um die Anwendung nutzen zu können, müssen Sie diese Tabellen mit Daten füllen. Dazu können Sie andere Anwendungen in der Composable MES App Suite verwenden, die Daten manuell eingeben, Automatisierungen nutzen oder Daten aus CSV-Dateien importieren.
Erforderliche Einstellungen
- Suchen Sie im Schritt "Dashboard" nach einem Auslöser namens "Heutige Variable speichern". Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Zeitzone mit Ihrer eigenen übereinstimmt.
- In den Schritten "Inspektionsergebnisse anzeigen" müssen Sie die Filter in der Analyse anpassen. Dadurch wird bestimmt, was im Analyse-Widget angezeigt wird. Sie können zum Beispiel den Filter "Typ" auf "manuelle Eingabe" oder auf eine beliebige Option setzen, die Sie in den anderen Anwendungen, die Sie zum Auffüllen der Tabellen verwenden, konfiguriert haben.
App-Struktur
Im Dashboard-Schritt können Benutzer grundlegende Analysen wie ausstehende Ereignisse, die Anzahl der heute geöffneten und geschlossenen Ereignisse und das Fehler-Pareto-Diagramm anzeigen.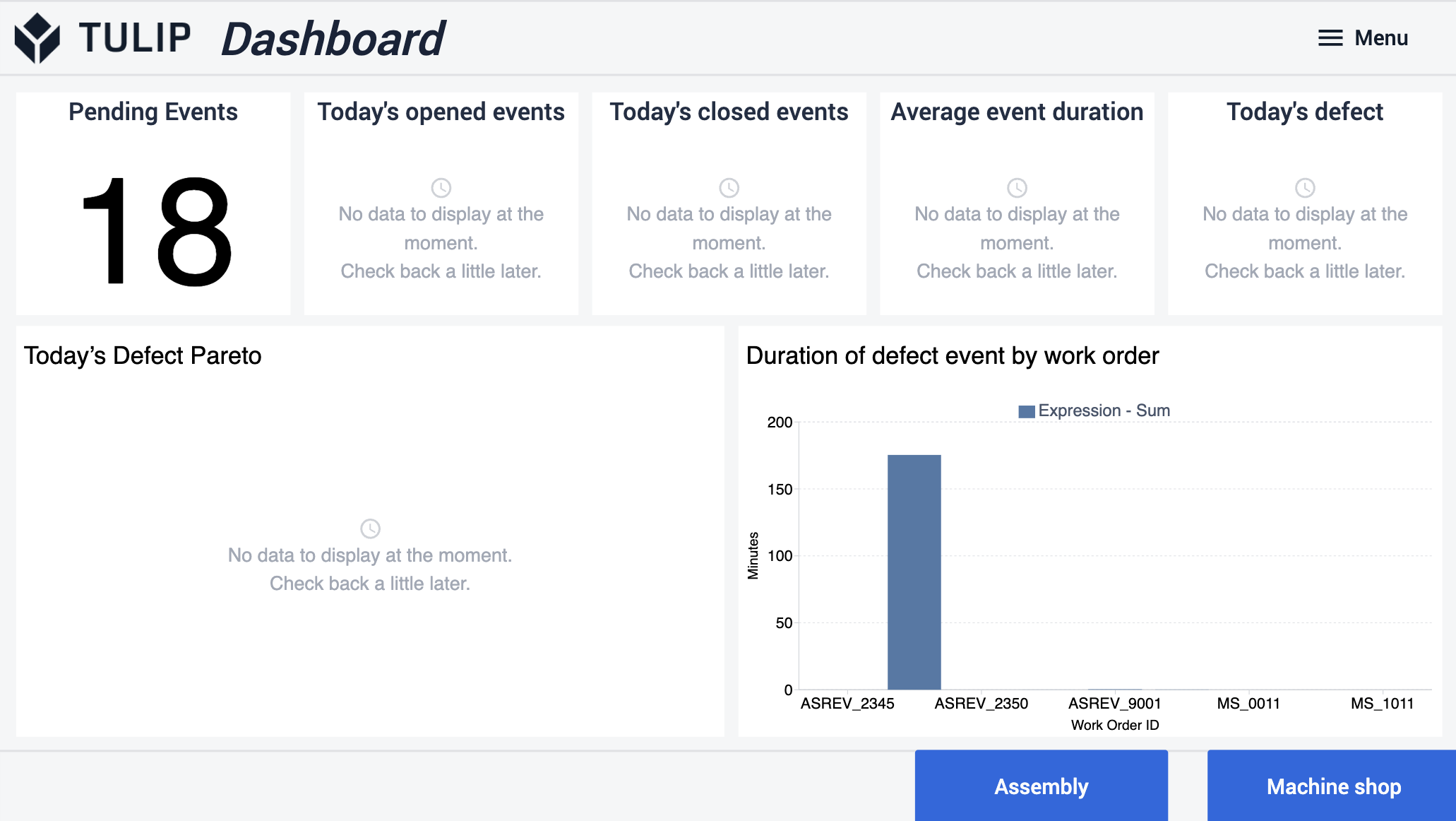
Die Benutzer haben die Möglichkeit, zu den nächsten Schritten zu navigieren, wo sie durch Auswahl eines Arbeitsauftrags oder einer Charge spezifische Analysen anzeigen können. In diesen Schritten können die Benutzer auch die Menge der Fehler für das ausgewählte Element sehen.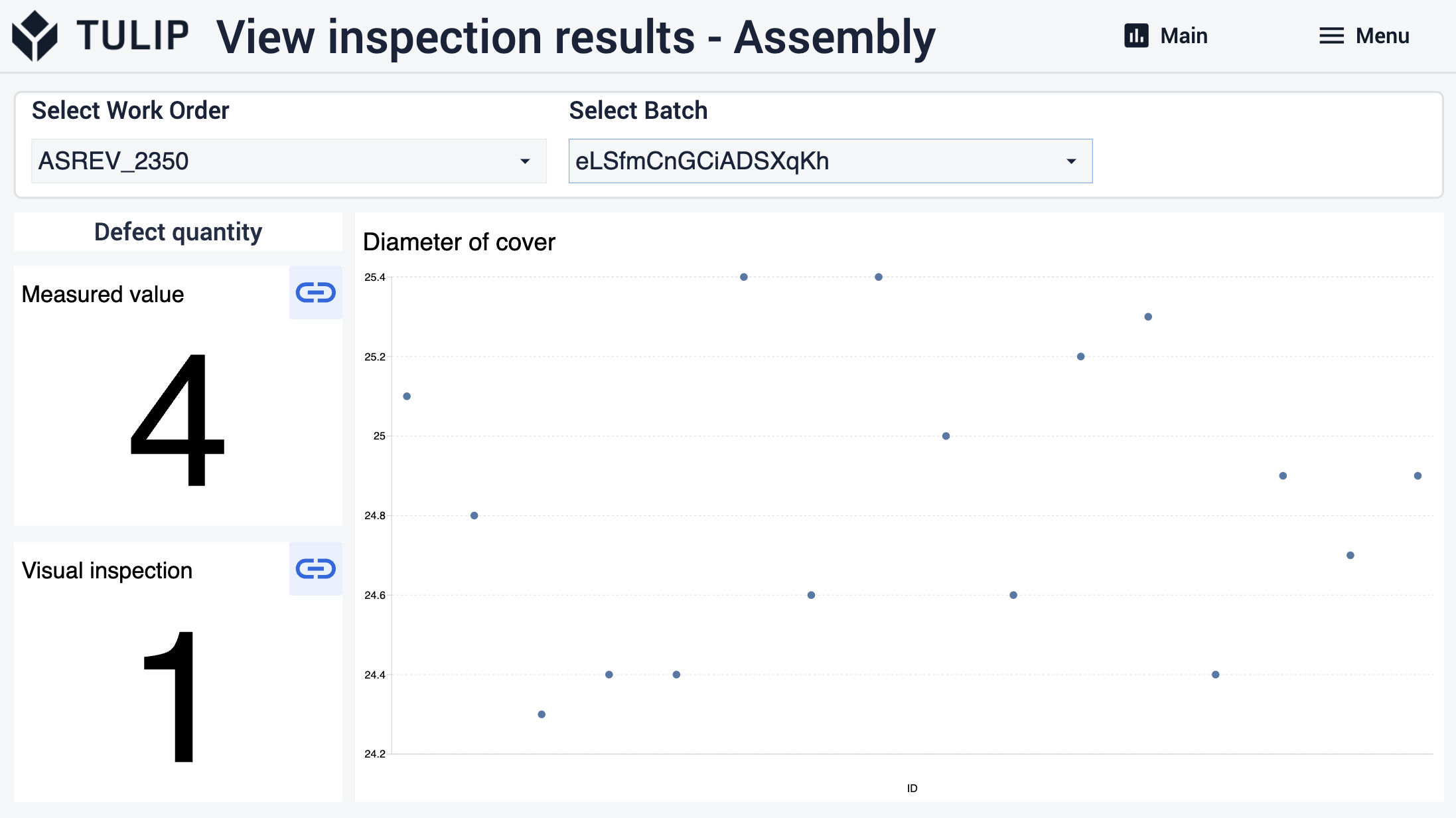
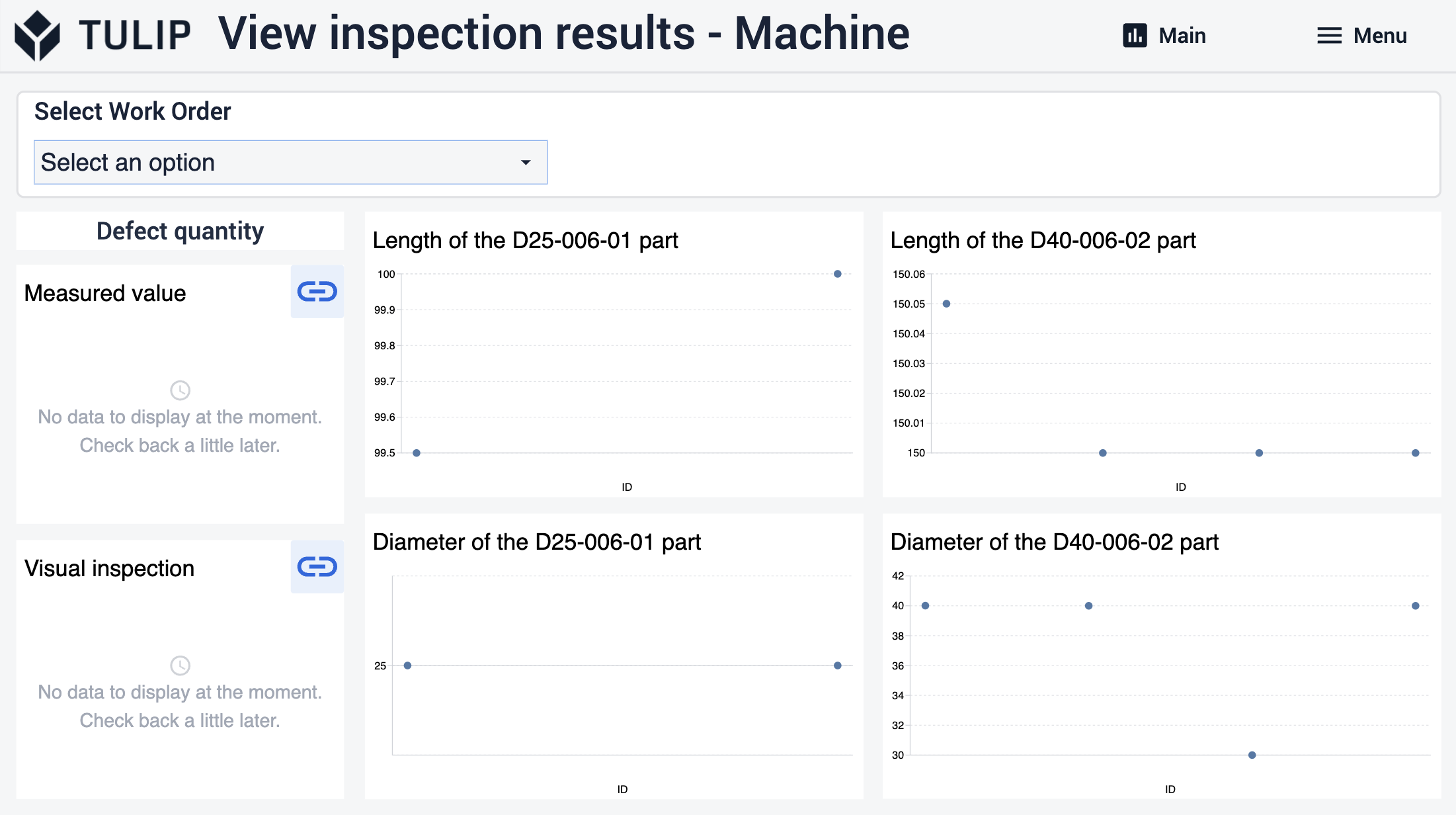
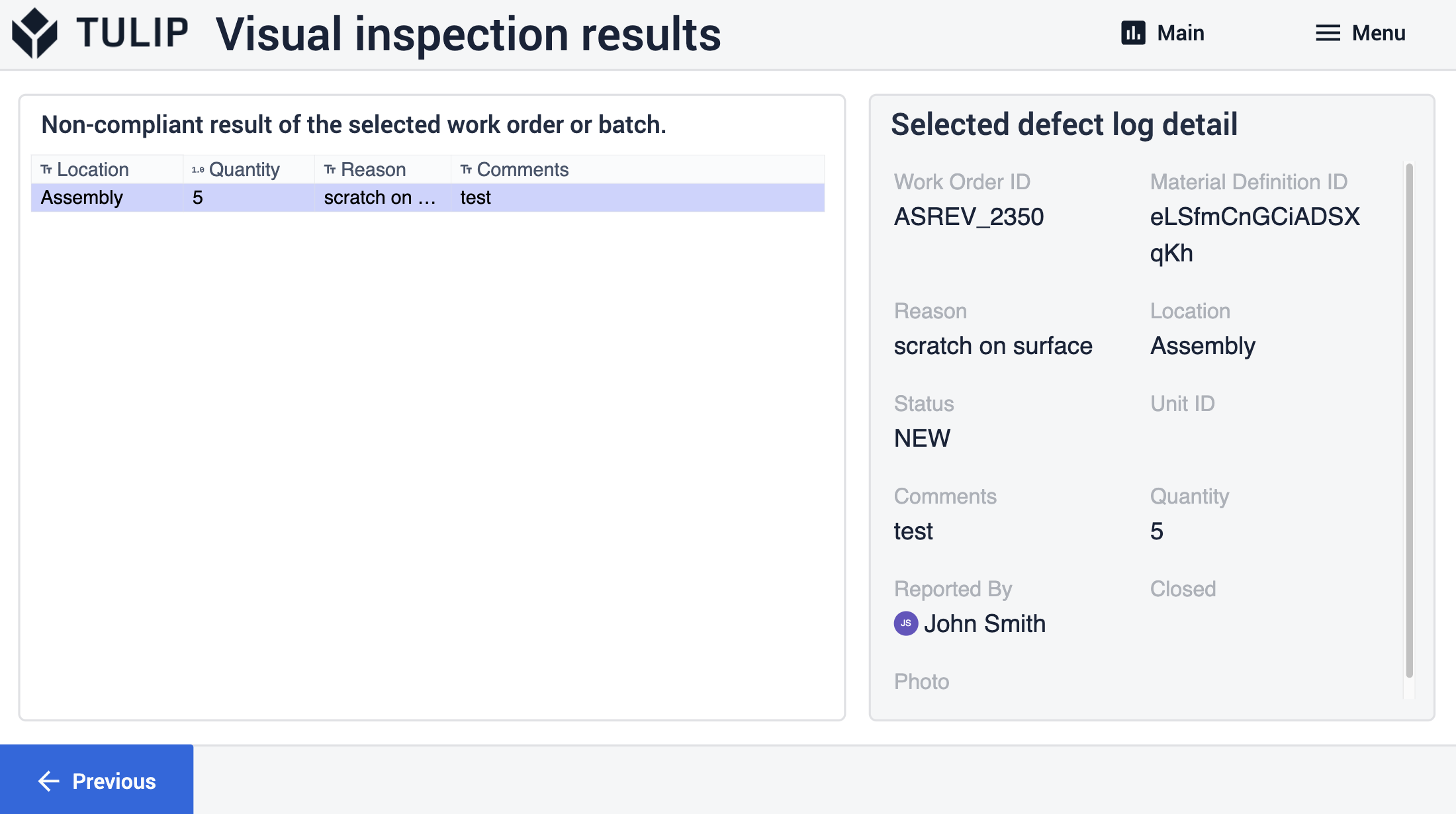
Wenn die Benutzer die Details der Mängel sehen möchten, können sie zu den Schritten navigieren, indem sie auf die Schaltflächen in der oberen rechten Ecke der Mängelfelder klicken.
In diesen Schritten werden alle nicht konformen Ergebnisse und ihre Werte für die Benutzer angezeigt. Durch Auswahl eines Datensatzes aus der Tabelle werden zusätzliche Informationen über den Fehler angezeigt.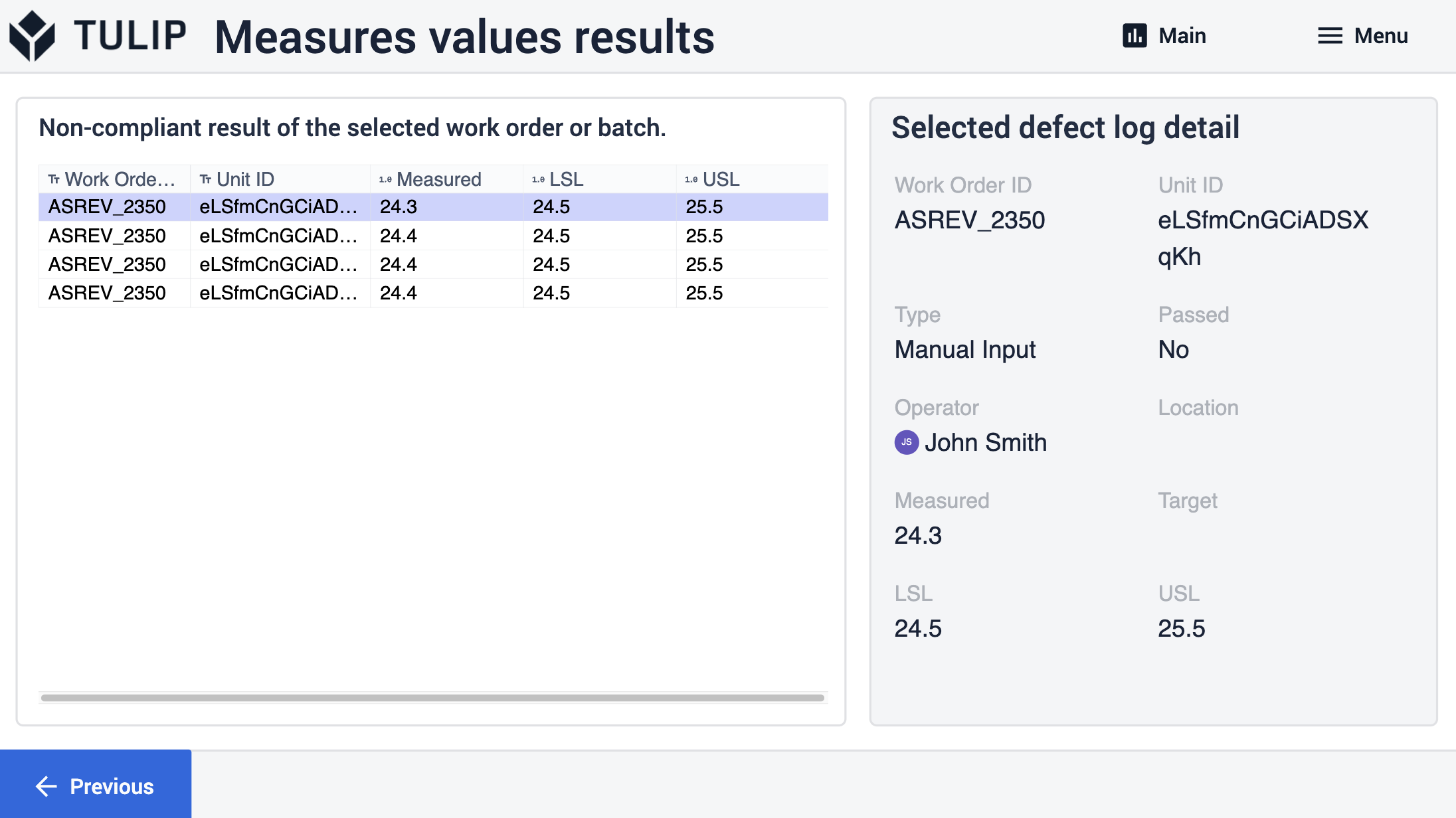
Erweiterte App-Verbindungen
Beispiele für die Verbindung von Anwendungen, die miteinander arbeiten.
Vorlage für die Qualitätsprüfung
Diese Anwendung stellt Daten aus den Prüfergebnissen und Fehlern zu den Chargen oder Arbeitsaufträgen zur Verfügung.
Auftragsverwaltung und Auftragsdurchführung
Verwenden Sie die Anwendungen Order Management und Order Execution aus der Composable MES App Suite. Erstere erstellt die Arbeitsaufträge, während die andere die abgeschlossenen Einheiten protokolliert und den Auftragsstatus aktualisiert.
