Ansible is an open source, command-line IT tool to bulk manage Edge device.
Learn more about Ansible here.
Who is this guide for
- Users with full Edge Device Permission
- Users familiar with Ansible
- Users familiar with setting up edge devices
How it works
Ansible is an IT-management software that allows you to copy and paste device configurations. This is accomplished by using a golden device as a verified, baseline configuration that will configure a target device.
For example, you can configure several new edge devices (the target devices) at one time by assigning the device to a group that automatically applies the credentials from an existing reference device (the golden device). You can update the golden device with further improvements and push out those updates.
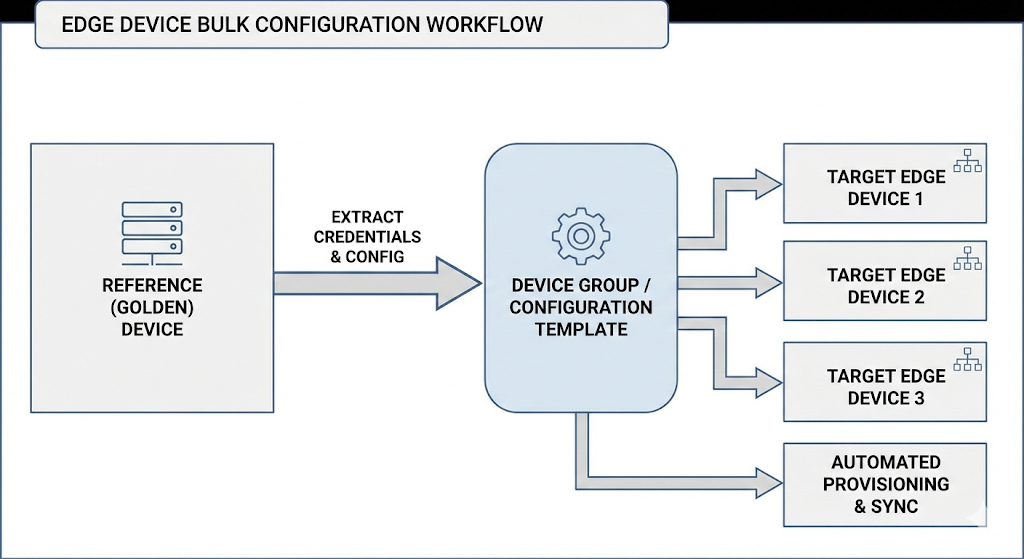
This method provides automated and scalable IT management, and reduces potential manual configuration errors.
Edge Device and Ansible integration
These procedures describe how to integrate Tulip Edge collection capabilities into your existing Ansible workflows.
Install the Tulip Edge collection
- Run the following command on your terminal:
ansible-galaxy collection install git+https://github.com/tulip/tulip-ansible-library.git#/collections/ansible_collections/tulip/edge
- To install the repository for edge devices, run the following command:
ansible-galaxy collection install tulip.edge
Inventory configuration
Add the following code to your existing inventory and fill in the variables.
- In the following code, name the device group and authenticate your instance with the instance’s URL, your email, and your email password.
[your_device_group:vars]
tulip_factory_url=https://your-factory.tulip.co
tulip_admin_email=admin@yourcompany.com
tulip_admin_password_sha256=your_sha256_hash
- In the following code, provide your company name.
tulip_client_name=YourCompanyName
tulip_client_version=1.0.0
tulip_client_description=Production Gateway
Generate a password hash
A password hash is a security measure that transforms a password into a fixed-length string of jumbled characters that cannot be easily reversed or deciphered. This step avoids the security risks associated with plaintext passwords in your file.
To generate secure password hashes, enter the following:
echo -n "your_password" | sha256sum | cut -d' ' -f1
Core playbook integration
Add necessary playbooks to your existing workflows with the following code:
- import_playbook: tulip.edge.gateway_tulip_auth
when: authenticate_with_factory | default(true)
- import_playbook: tulip.edge.register
when: register_devices | default(false)
Testing integration
Add a testing playbook to your workflows with the following code:
- name: Test Tulip Gateway Authentication
hosts: test_devices
tasks:
- name: Authenticate test device
import_playbook: collections/ansible_collections/tulip/edge/playbooks/gateway_tulip_auth.yml
- name: Verify authentication worked
import_playbook: collections/ansible_collections/tulip/edge/playbooks/gateway_device_info.yml
- name: Check connectivity
import_playbook: collections/ansible_collections/tulip/edge/playbooks/gateway_check_internet.yml
Integration best practices
-
Variable management
- Use group_vars for common settings
- Use host_vars for device-specific overrides
- Store sensitive data in Ansible Vault
-
Error handling
- name: Authenticate with factory
import_playbook: gateway_tulip_auth.yml
ignore_errors: true
register: auth_result
- name: Handle authentication failure
debug:
msg: "Authentication failed, check credentials"
when: auth_result.failed | default(false)
-
Backup management
- Use consistent backup naming, such as:
device-component-timestamp - Store backup names in variables for reuse
- Implement backup retention policies
- Use consistent backup naming, such as:
-
Maintain idempotency
All playbooks are idempotent and therefore safe to run multiple times.
To find errors, understand logic execution, or validate before execution, you can do a practice run, which will not run the actual software. To do a practice run, use --check mode, shown in the example below.
ansible-playbook gateway_tulip_auth.yml --limit test_device --check
Golden device provisioning
The golden device provisioning workflow allows you to:
- Select a golden device: Choose a properly configured reference device
- Backup golden configuration: Capture all component configurations
- Deploy to new devices: Apply golden device settings to new/replacement devices
- Authenticate and verify: Register devices and validate deployment
Inventory configuration
Configure your inventory with the golden device and target devices.
Enter the following in your terminal:
[tulip_edge_devices]
golden-device ansible_host=172.16.15.130
EIO-01-BCDEFA ansible_host=172.16.15.140
EIO-01-CDEFAB ansible_host=172.16.15.141
EIO-01-DEFABCansible_host=172.16.15.150
[golden_devices]
EIO-01-ABCDEF
[newly_provisioned]
EIO-01-BCDEFA
EIO-01-CDEFAB
EIO-01-DEFABC
[tulip_edge_devices:vars]
# Factory Authentication
tulip_factory_url=https://your-factory.tulip.co
tulip_admin_email=admin@yourcompany.com
tulip_admin_password_sha256=your_sha256_hash
# Client Information
tulip_client_name=YourCompanyName
tulip_client_version=1.0.0
tulip_client_description=Production Gateway
Generate password hash
A password hash is a security measure that transforms a password into a fixed-length string of jumbled characters that cannot be easily reversed or deciphered. This step avoids the security risks associated with plaintext passwords in your file.
To create a SHA256 hash for secure password storage, enter the following:
echo -n "your_password" | sha256sum | cut -d' ' -f1
Basic golden device provisioning
Enter the following code for each step.
- Log in to your golden device
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.login --limit golden-device
- Backup the golden device’s configurations
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.backup_mqtt_broker --limit golden-device
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.backup_mqtt_bridge --limit golden-device
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.backup_drivers --limit golden-device
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.backup_root_certs --limit golden-device
- Log in to the target devices
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.login --limit newly_provisioned
- Deploy golden configurations to target devices
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.restore_mqtt_broker \
--limit newly_provisioned \
-e mqtt_broker_backup_name="golden-device-mqtt-broker-20241219-143022"
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.restore_mqtt_bridge \
--limit newly_provisioned \
-e mqtt_bridge_backup_name="golden-device-mqtt-bridge-20241219-143025"
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.restore_drivers \
--limit newly_provisioned \
-e drivers_backup_name="golden-device-drivers-20241219-143028"
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.restore_root_certs \
--limit newly_provisioned \
-e root_certs_backup_name="golden-device-root-certs-20241219-143030"
- Authenticate with factory
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.gateway_tulip_auth --limit newly_provisioned
- Register with external systems (optional)
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.register --limit newly_provisioned
- Verify deployment
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.gateway_device_info --limit newly_provisioned
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.gateway_check_internet --limit newly_provisioned
Golden device best practices
The following golden device approach ensures consistent, reliable provisioning of your Tulip Edge device fleet while maintaining full traceability and control over your configuration standards.
- Maintain the golden device: Keep your golden device updated and well-maintained
- Create regular backups: Create regular backups of your golden device configuration
- Ensure version control: Store golden device backups in version control with meaningful names
- Have a testing pipeline: Always test golden device configurations in staging before production
- Document the golden device configuration: Document your golden device configuration standards and procedures
- Ensure access control: Limit access to golden devices and use separate credentials
- Monitor health and processes: Monitor golden device health and backup creation processes
Troubleshoot
Here’s how to troubleshoot common golden device issues:
The golden device is unreachable
First, test your connectivity to the golden device. Run:
ansible golden-device -m ping
Check the golden device status. Run:
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.gateway_device_info --limit golden-device
The backup deployment is failing
First, you should verify that the backup file exists. Run:
ls backups/golden-device-mqtt-broker-*.json
Use backup naming with extension
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.restore_mqtt_broker \
--limit target-device \
-e mqtt_broker_backup_name="golden-device-mqtt-broker-20241219-143022" \
-vv
Authentication issues
To re-authenticate the golden device, run:
ansible-playbook tulip.edge.login --limit golden-device
To verify the golden device credential in your inventory, run:
ansible-inventory --host golden-device
Did you find what you were looking for?
You can also head to community.tulip.co to post your question or see if others have solved a similar topic!
