Overview
When passing information to other systems, you may need additional control on how those Inputs are encoded before passing that information to other systems. By default, Tulip will attempt to use the most common encoding method, but you can override this to better fit your needs.
Your app builders continue to work with the standard Tulip Variables, and connector configuration will modify their inputs to fit your integration needs.
How to
Inputs that allow custom encoding will show up with an encoding pill next to each input. When clicked, these pills will allow you to select an encoding option.
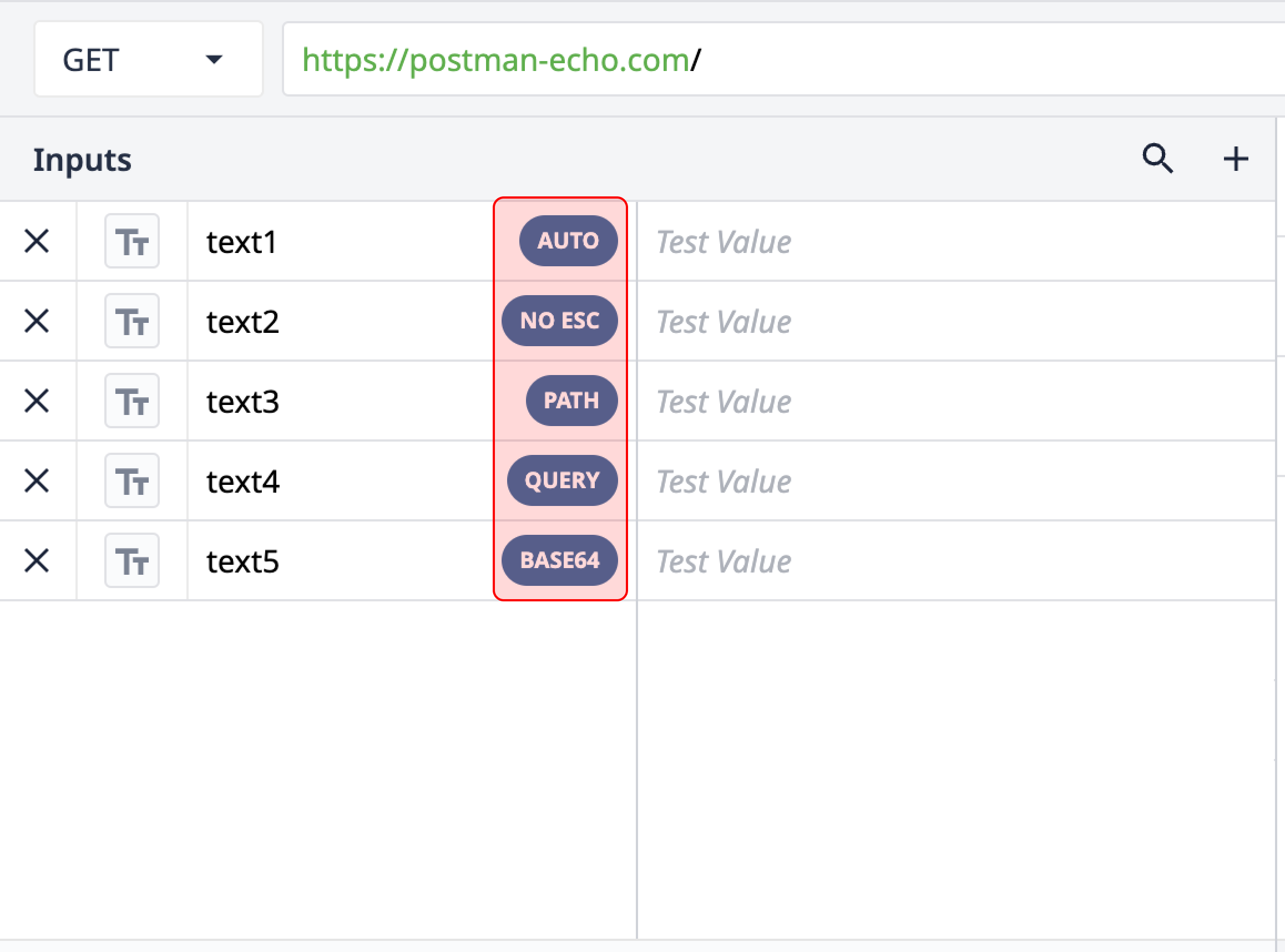
Encoding Options - Text Inputs
Automatic encoding
Characters will be escaped according to the location of usage.
In the URL path: Path encoding
In the query: Query encoding
In the Header: No encoding
In the body: No encoding
No encoding
No characters will be escaped.
This may cause errors if any characters besides the following are passed through:
A-Z a-z 0-9 - _ . ! ~ * ' ( )".
Path encoding
All characters except the following will be escaped:
A-Z a-z 0-9 ; , / ? : @ & = + $ - _ . ! ~ * ' ( ) #
Query encoding
All characters except the following will be escaped:
A-Z a-z 0-9 - _ . ! ~ * ' ( )
Base64 encoding
The text will be encoded using Base64.
Encoding Options - Image Inputs
Custom image encoding functionality is actively being rolled out. Reach out to support@tulip.co if you would like it enabled.
Images stored wtihin Tulip are stored in our cloud storage services, and references to these images are dynamically generated in your applications and Tulip tables. These references expire every 3 hours. When passing these images to external systems, you may want to encode them in another format so they do not expire.
Clicking on the encoding pill for any input will allow you to configure its encoding.
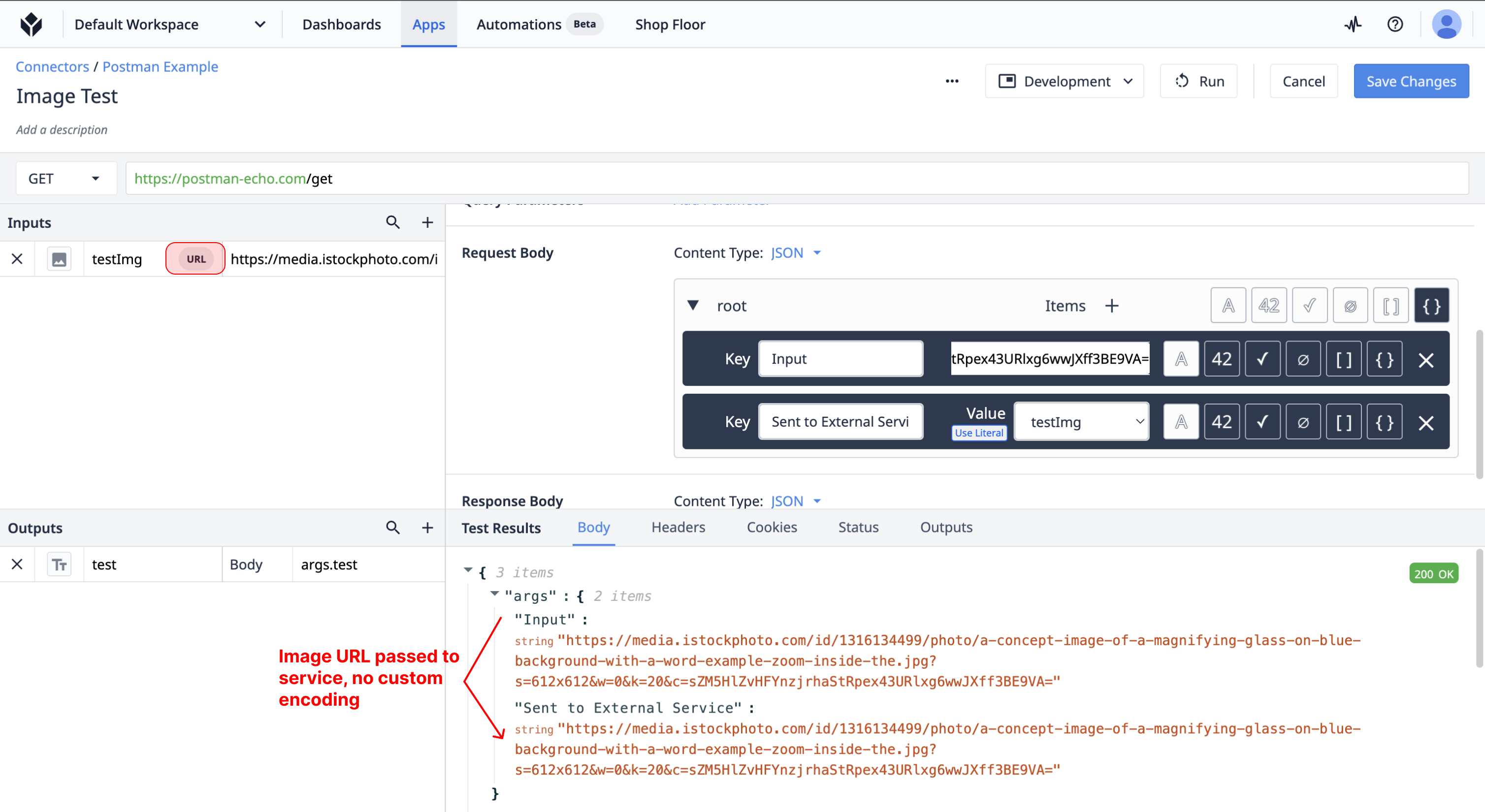
Image URL Encoding
By default, image inputs to connectors will be passed as the signed URL to the respective image. This input can be used in your connector anywhere a text input can be used.
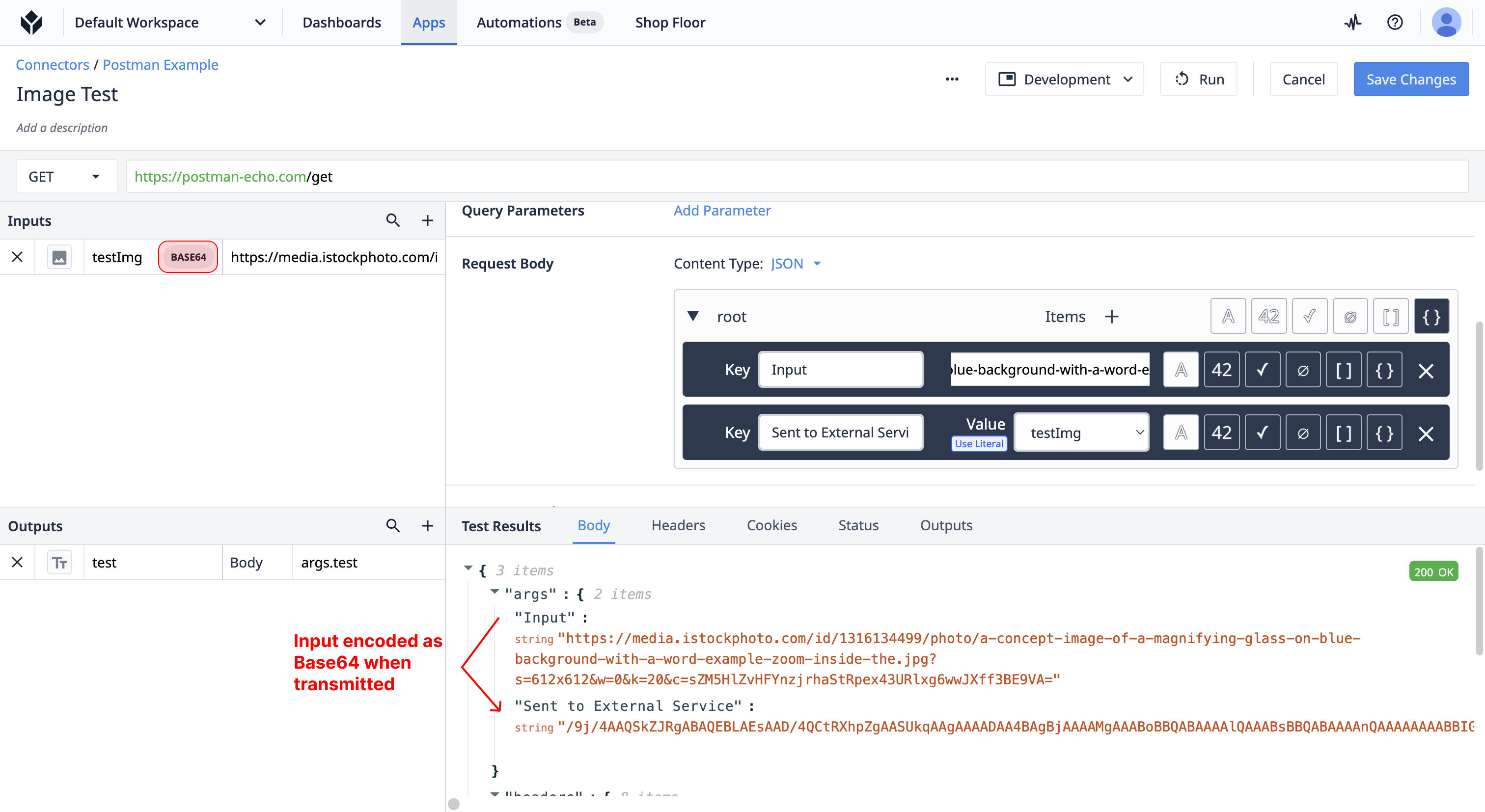
Base64 Encoding
Base64 is one of the simplest standards for encoding binary data, and is a common standard for transfering small files over http calls. When Base64 is selected, any image input will automatically be encoded as base64 before being sent to the external service.
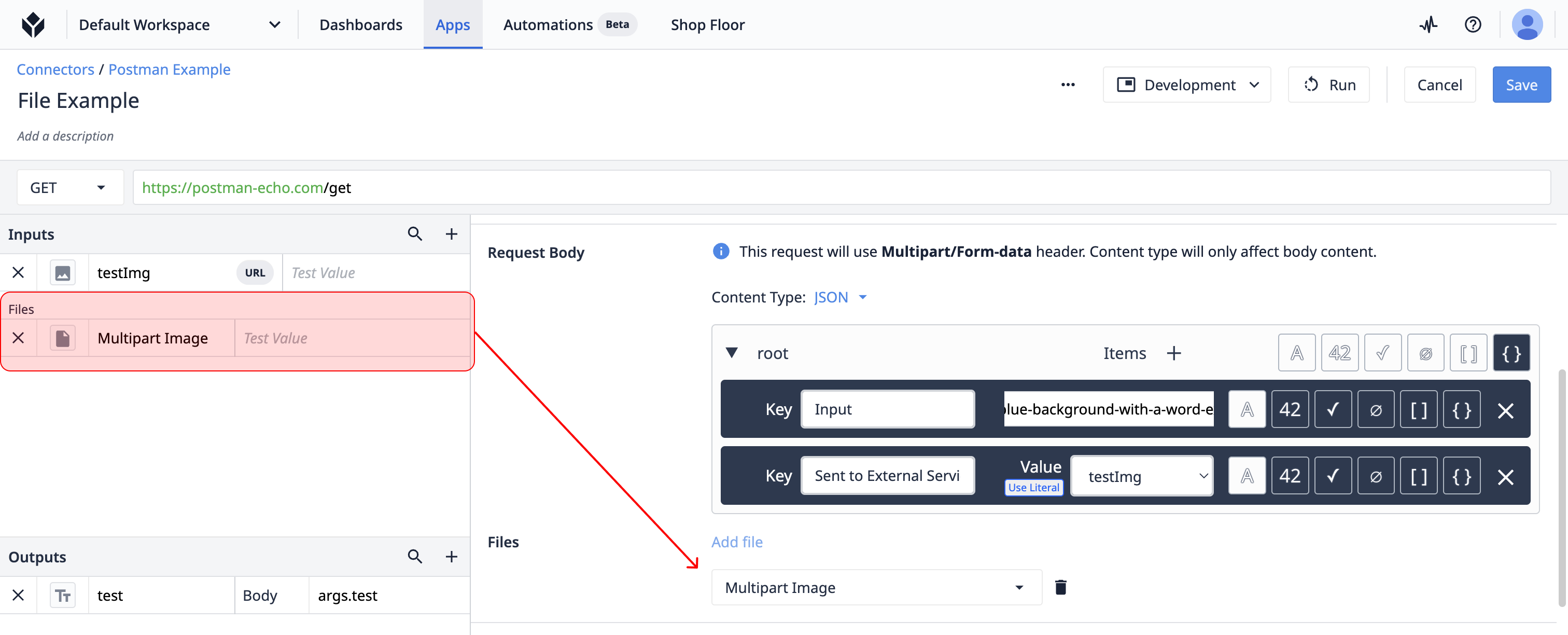
File Encoding
Multipart/form-data is another very common format for passing binary data. This is more common for larger files. Click on the "File" option to change the encoding of this input. This will automatically move the input down into the "Files" input section. These inputs cannot be used outside of the payload body.
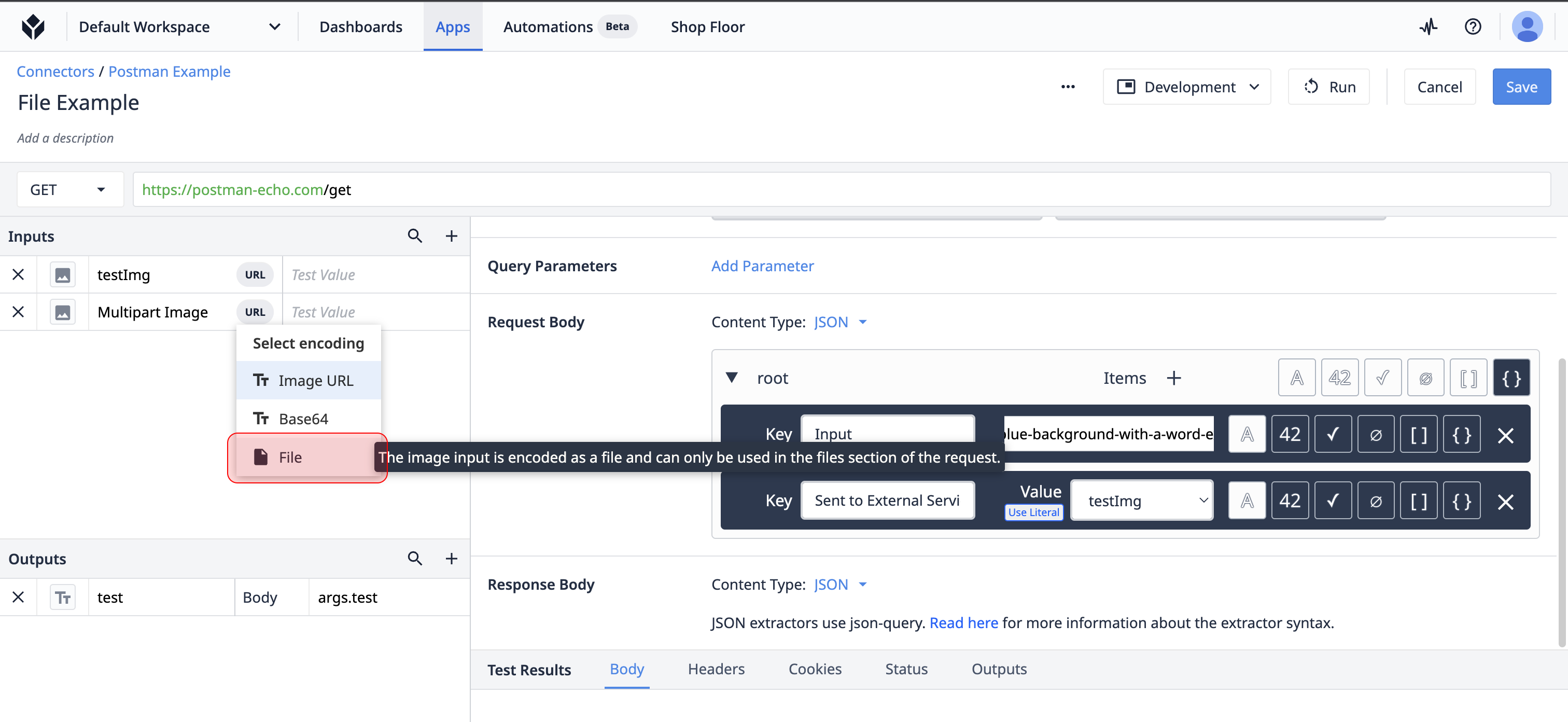
This data type is not encoded as text, so it cannot be used within a json payload. Instead, a "files" section will be added to the request body section. Files can be added or removed here.
Encoding Options - Datetime Input Encoding Options
Epoch Seconds
The number of seconds that have elapsed since the Unix epoch, which is January 1, 1970, at 00:00:00 Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
Epoch Milliseconds
The number of milliseconds that have elapsed since the Unix epoch, which is January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 UTC.
ISO 8601 RFC 3339
Standard format: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ssZ . Indicates UTC with the 'Z'.

